Line Drawing 1

Figs 61-65. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., tentacular armature: 61, internal surface, metabasal region; 62, external surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 63, internal surface,... MoreFigs 61-65. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., tentacular armature: 61, internal surface, metabasal region; 62, external surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 63, internal surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 64, bothridial surface, internal surface, internal surface on right-hand side, basal and metabasal region; 65, oblique view of internal surface of metabasal and basal armature, bothridial surface on left-hand side. Scale line, 0.1mm. |
Line Drawing 2
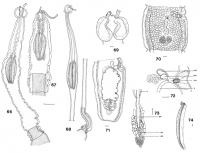
Figs 66-68. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., scolex, showing variation in position of bulbs and length of pars post bulbosa and velum in specimens which were contracted (66, 67) or relaxed (68).... MoreFigs 66-68. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., scolex, showing variation in position of bulbs and length of pars post bulbosa and velum in specimens which were contracted (66, 67) or relaxed (68). Scale line, 1.0mm. Figs 69-74. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov.: 69, scolex, 70, mature proglottis; 71, gravid proglottis; 72, male genital ducts; 73, female genital complex; 74, bulb. Scale lines, 0.1mm. Abbreviations as for Figs 21-28; UD, uterine duct. Abbreviations: ASV, accessory seminal vesicle; DOC, dorsal osmoregulatory canal; ESV, external seminal vesicle; FD, fertilisation duct; ISV, internal seminal vesicle; O, ovary; OI, ovarian isthmus; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; U, uterus; V, vagina; VC, vitelline canal; VOC, ventral osmoregulatory canal; VR, vitelline reservoir. |
Photo Micrograph
|
Scanning Electron Micrograph
|
 Global Cestode Database
Global Cestode Database



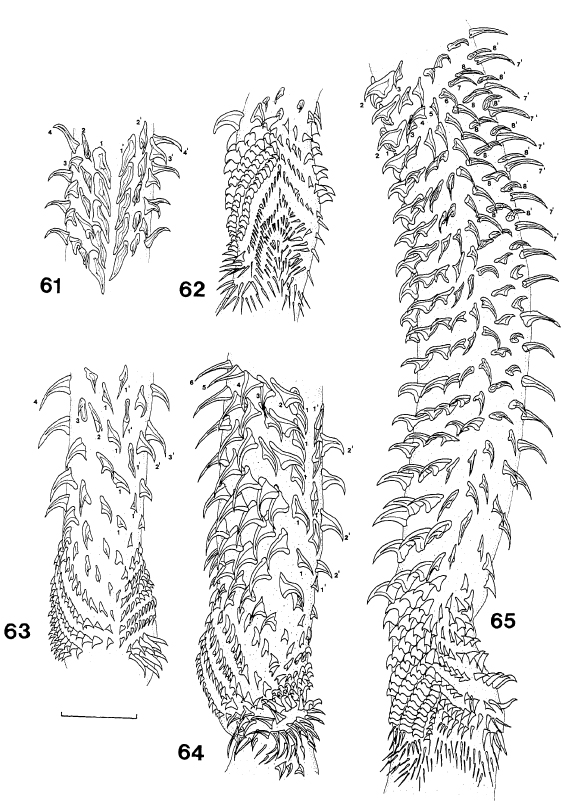 Figs 61-65. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., tentacular armature: 61, internal surface, metabasal region; 62, external surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 63, internal surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 64, bothridial surface, internal surface, internal surface on right-hand side, basal and metabasal region; 65, oblique view of internal surface of metabasal and basal armature, bothridial surface on left-hand side. Scale line, 0.1mm.
Figs 61-65. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., tentacular armature: 61, internal surface, metabasal region; 62, external surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 63, internal surface, transition from basal to metabasal armature; 64, bothridial surface, internal surface, internal surface on right-hand side, basal and metabasal region; 65, oblique view of internal surface of metabasal and basal armature, bothridial surface on left-hand side. Scale line, 0.1mm. 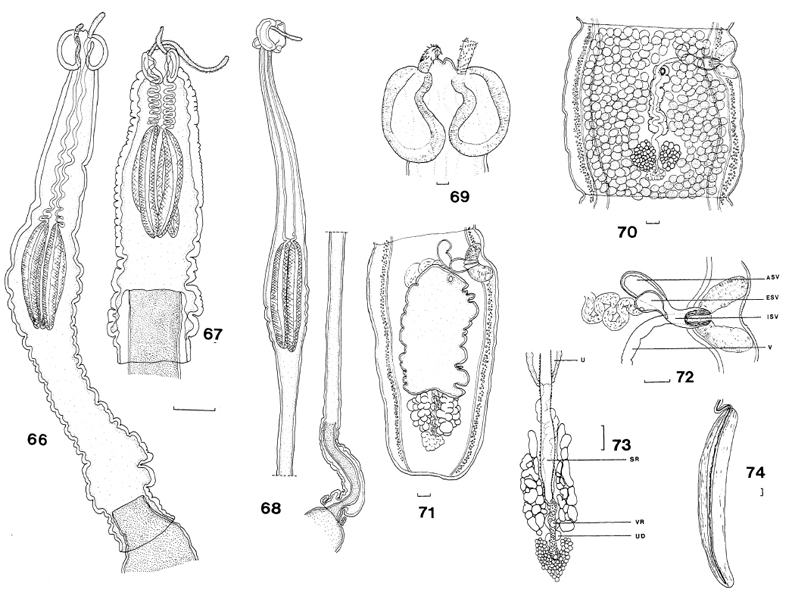 Figs 66-68. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., scolex, showing variation in position of bulbs and length of pars post bulbosa and velum in specimens which were contracted (66, 67) or relaxed (68). Scale line, 1.0mm. Figs 69-74. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov.: 69, scolex, 70, mature proglottis; 71, gravid proglottis; 72, male genital ducts; 73, female genital complex; 74, bulb. Scale lines, 0.1mm. Abbreviations as for Figs 21-28; UD, uterine duct. Abbreviations: ASV, accessory seminal vesicle; DOC, dorsal osmoregulatory canal; ESV, external seminal vesicle; FD, fertilisation duct; ISV, internal seminal vesicle; O, ovary; OI, ovarian isthmus; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; U, uterus; V, vagina; VC, vitelline canal; VOC, ventral osmoregulatory canal; VR, vitelline reservoir.
Figs 66-68. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov., scolex, showing variation in position of bulbs and length of pars post bulbosa and velum in specimens which were contracted (66, 67) or relaxed (68). Scale line, 1.0mm. Figs 69-74. Deanicola protentus, gen. et sp. nov.: 69, scolex, 70, mature proglottis; 71, gravid proglottis; 72, male genital ducts; 73, female genital complex; 74, bulb. Scale lines, 0.1mm. Abbreviations as for Figs 21-28; UD, uterine duct. Abbreviations: ASV, accessory seminal vesicle; DOC, dorsal osmoregulatory canal; ESV, external seminal vesicle; FD, fertilisation duct; ISV, internal seminal vesicle; O, ovary; OI, ovarian isthmus; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; U, uterus; V, vagina; VC, vitelline canal; VOC, ventral osmoregulatory canal; VR, vitelline reservoir. 

