Line Drawing 1
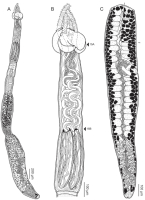
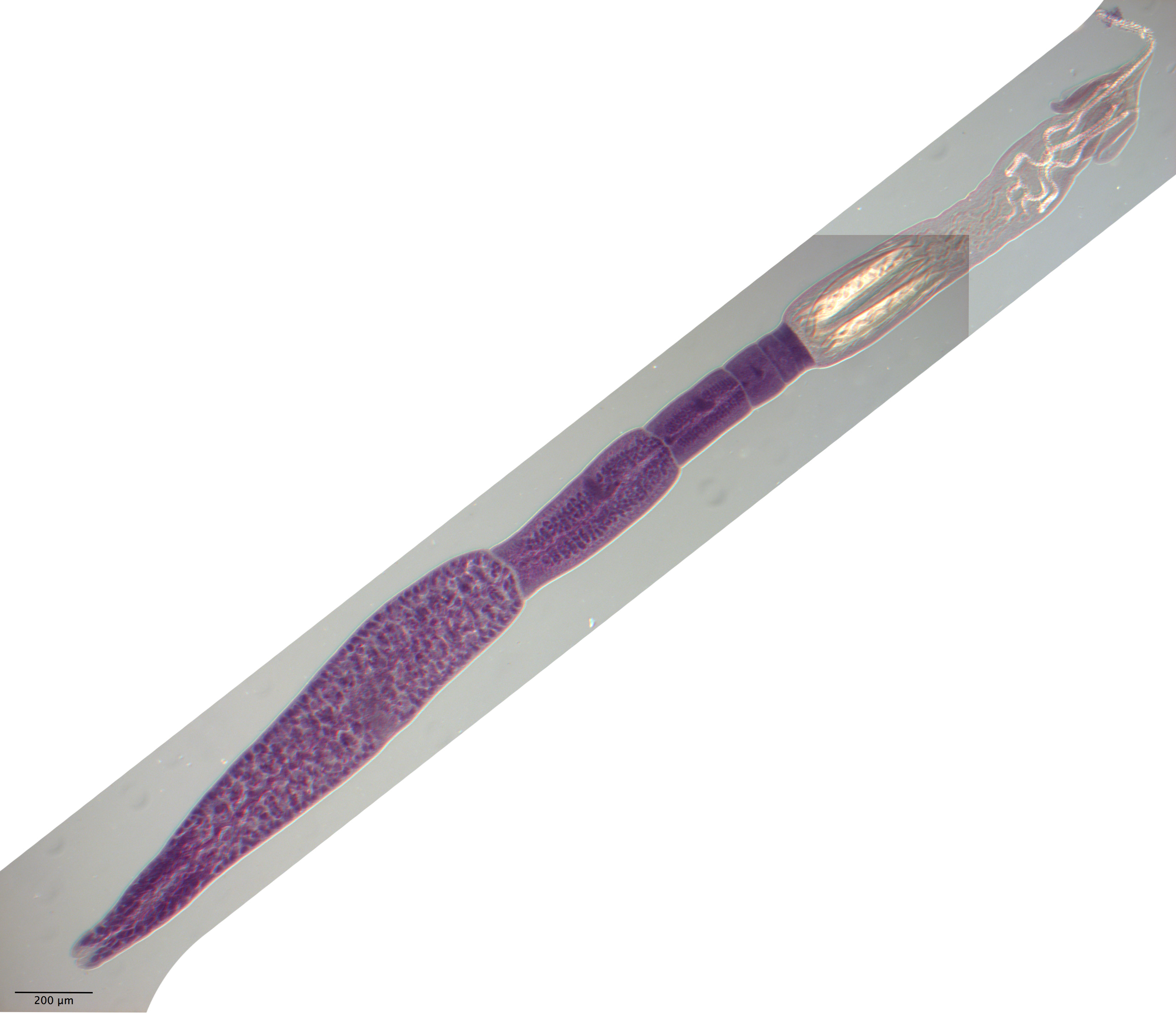
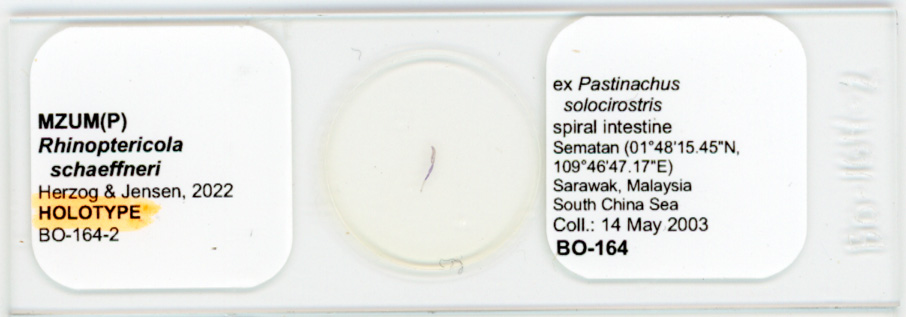
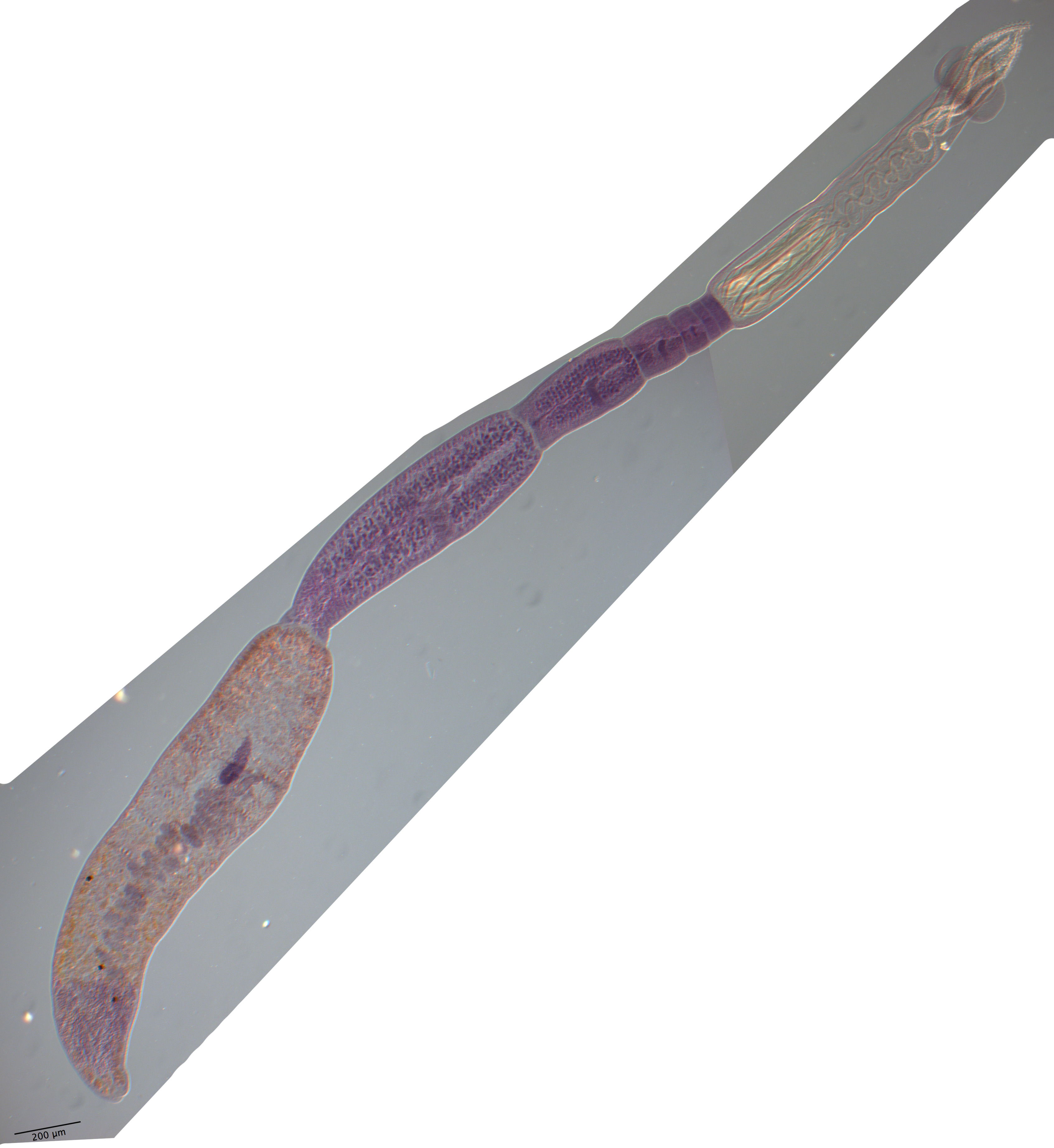
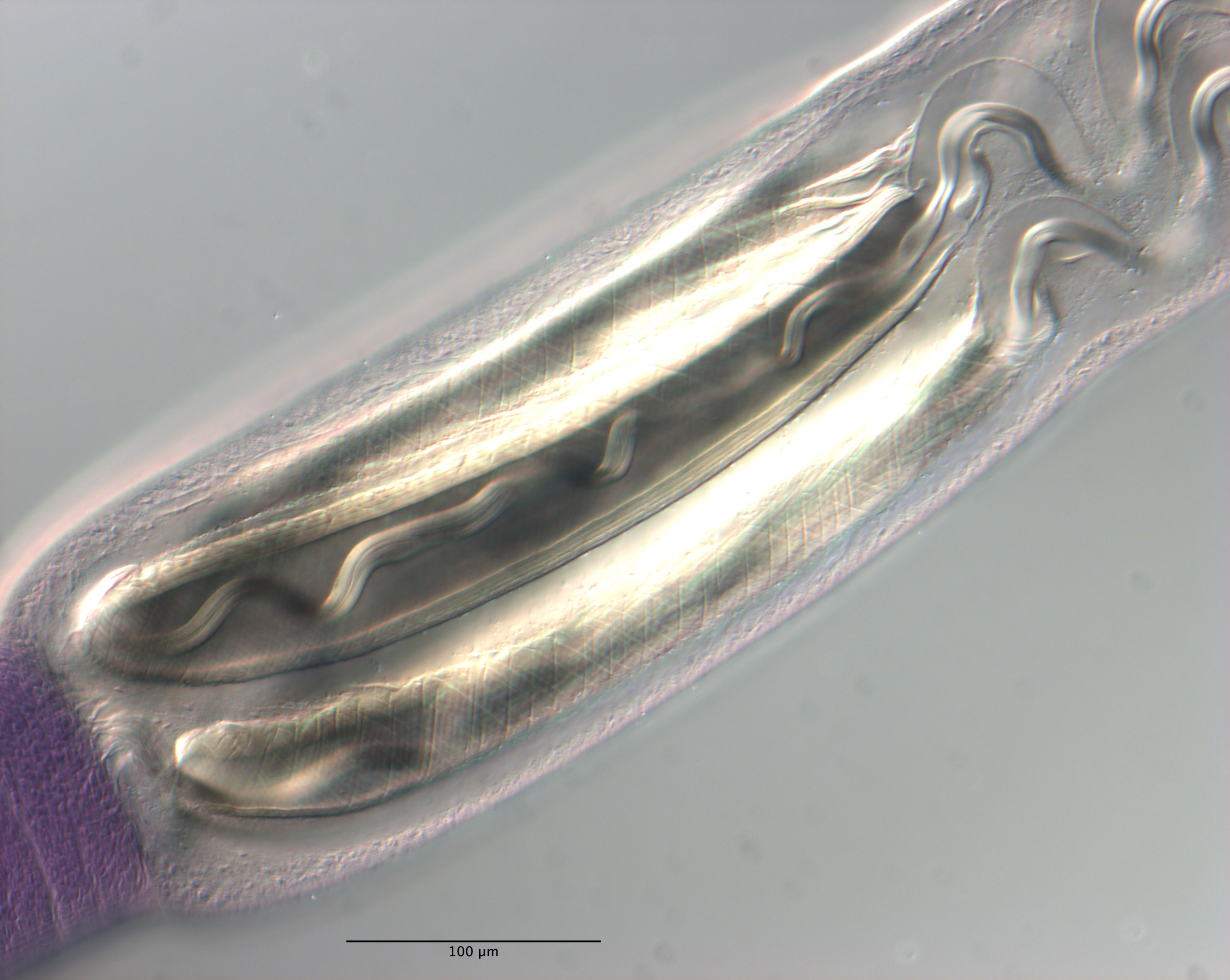
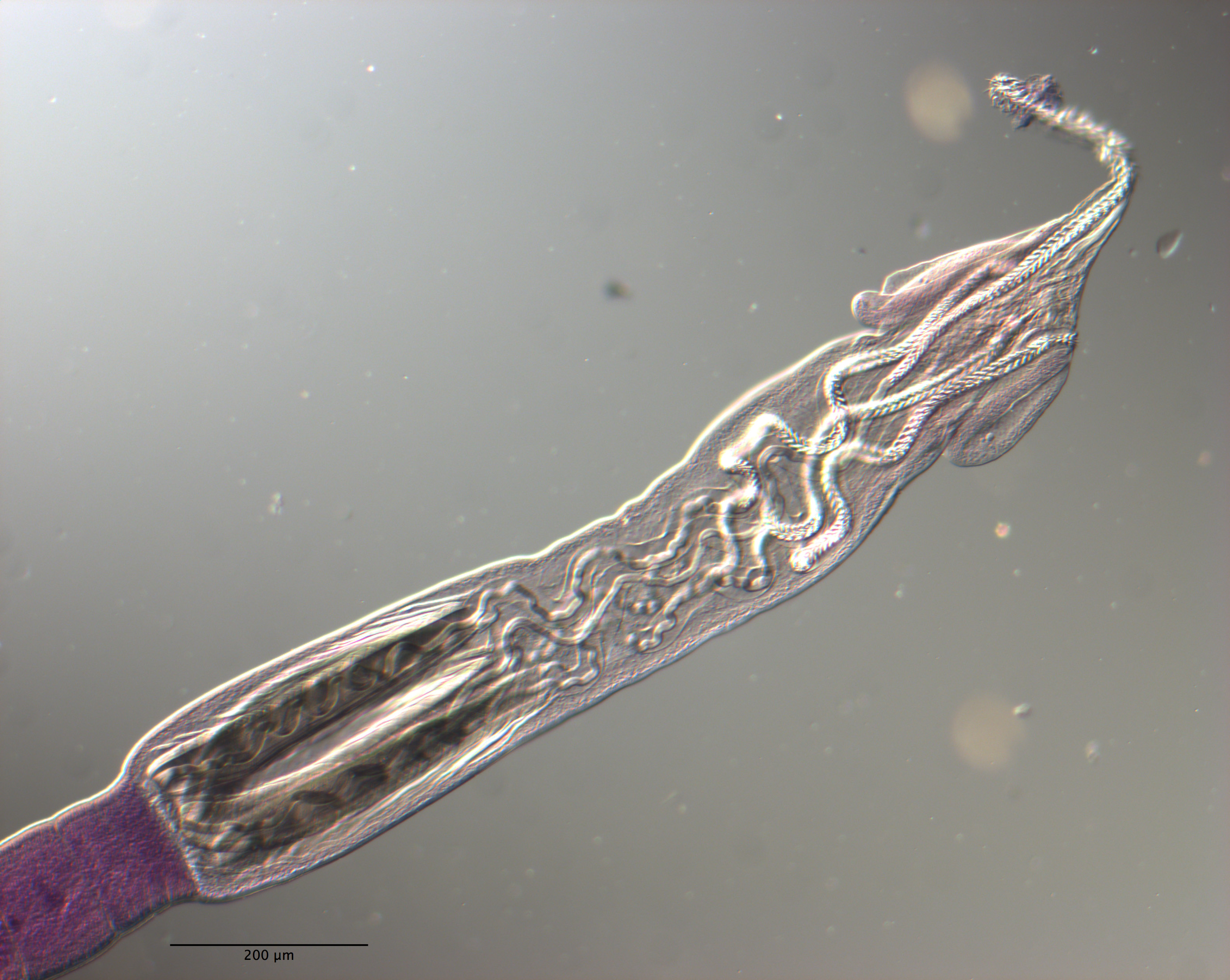
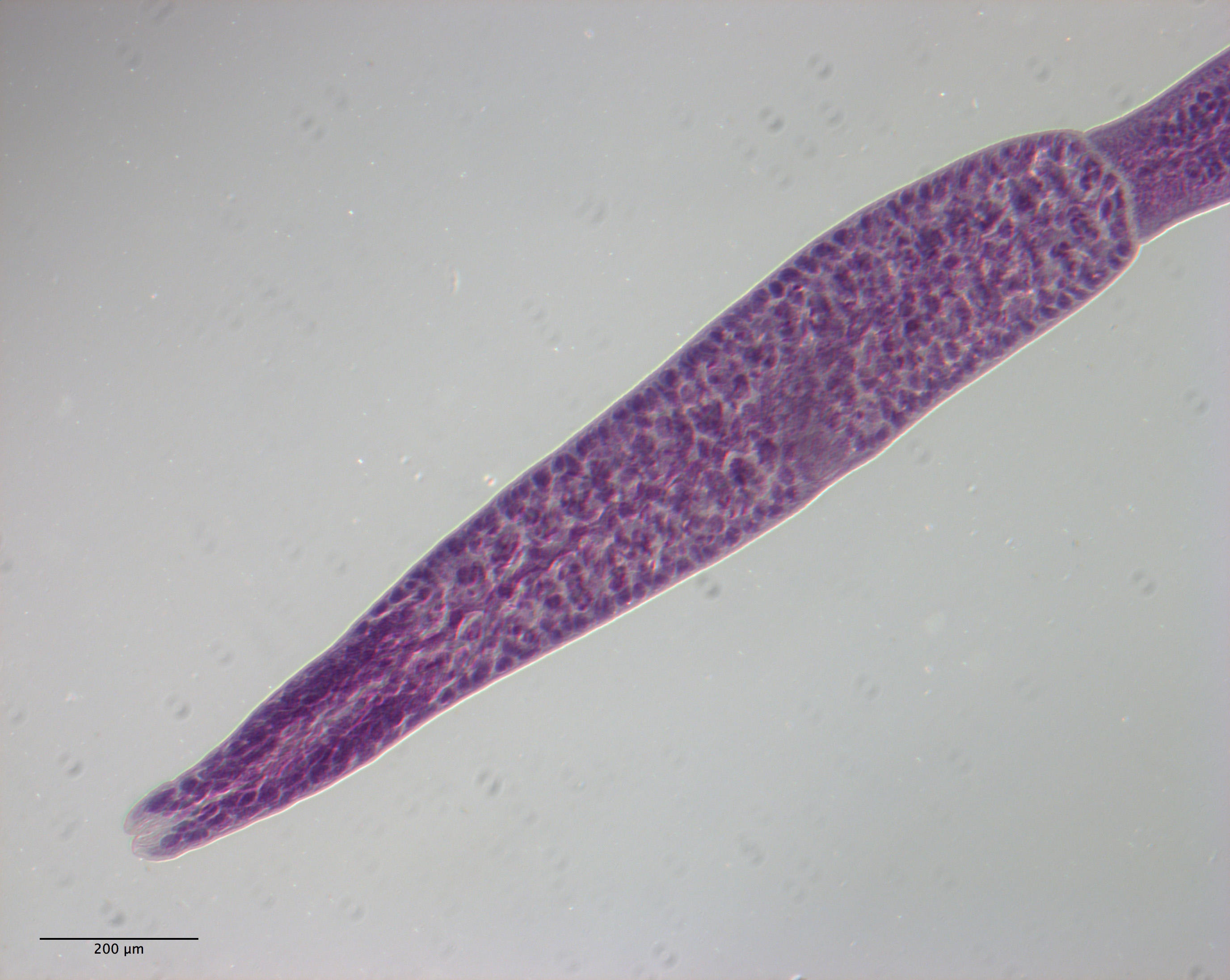
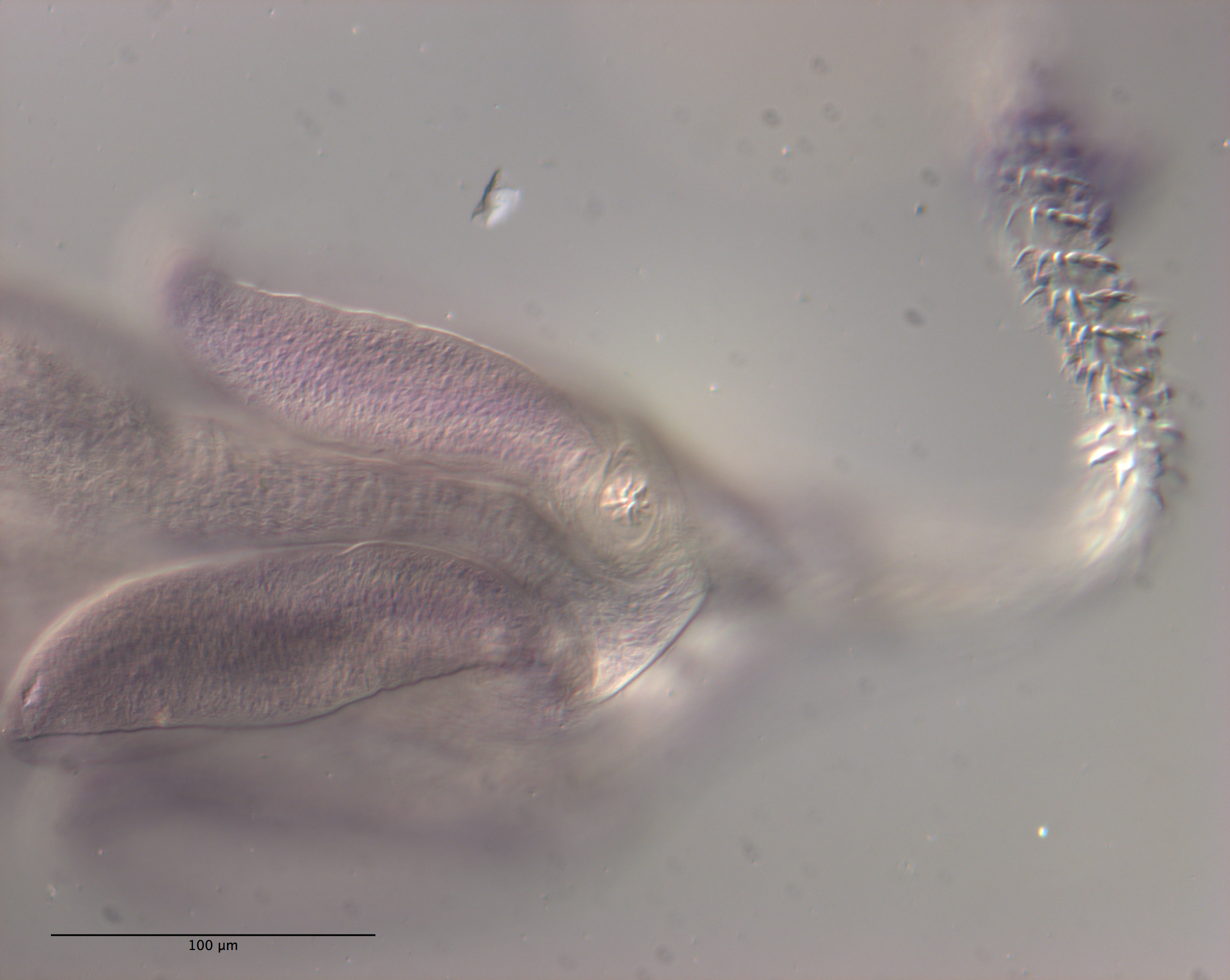
Figure 11 Line drawings of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Whole worm (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H];
holotype). (B) Scolex (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H]; holotype); arrowheads indicate the level at which the secti... MoreFigure 11 Line drawings of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Whole worm (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H];
holotype). (B) Scolex (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H]; holotype); arrowheads indicate the level at which the sections in Fig. 15 were taken. (C) Terminal proglottid (USNM 1661588; paratype); circumcortical vitelline follicles are drawn only on the lateral margins and in the region delimited by dashed lines. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-11 |
Line Drawing 2
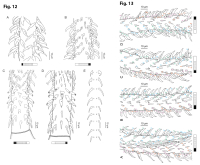
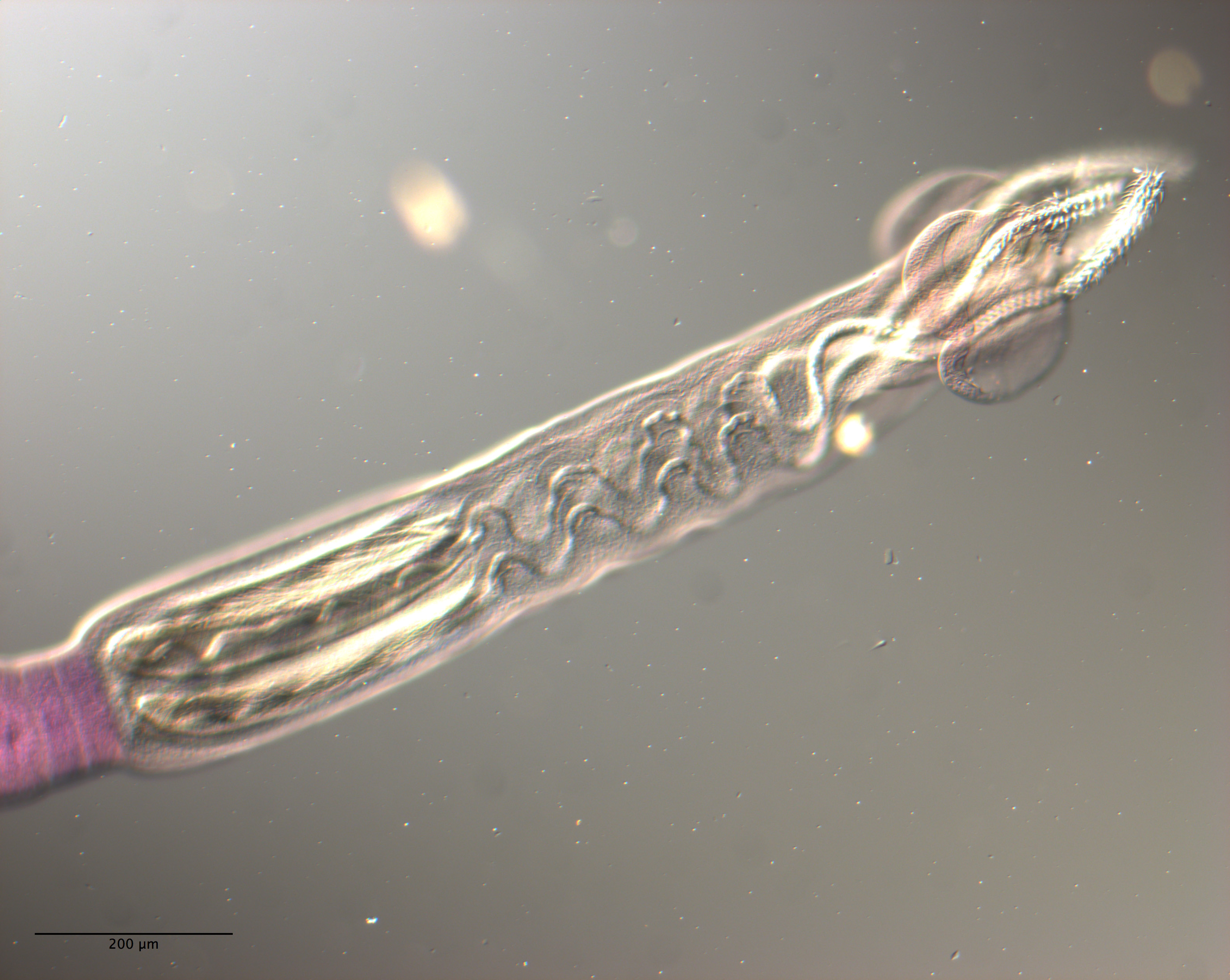
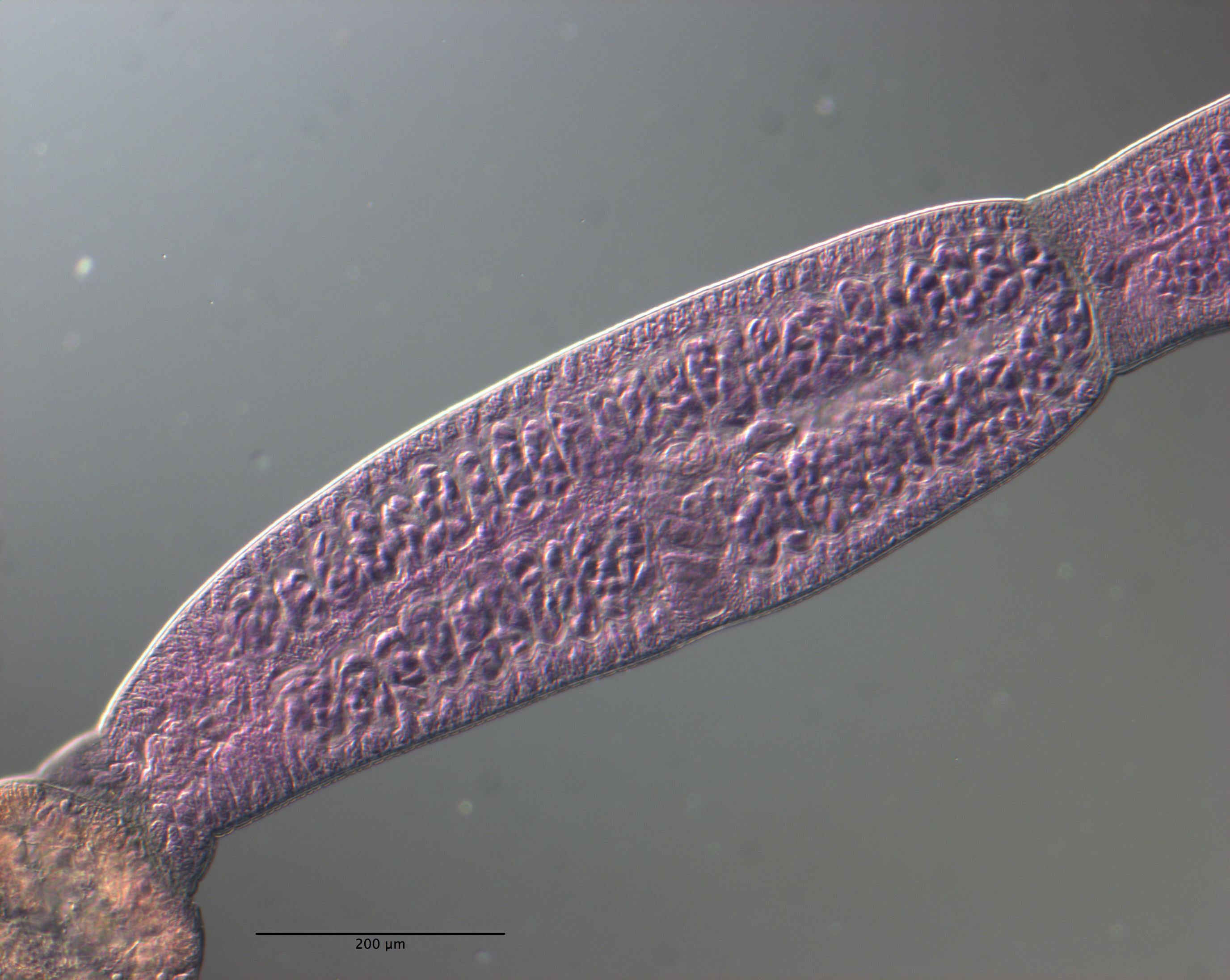
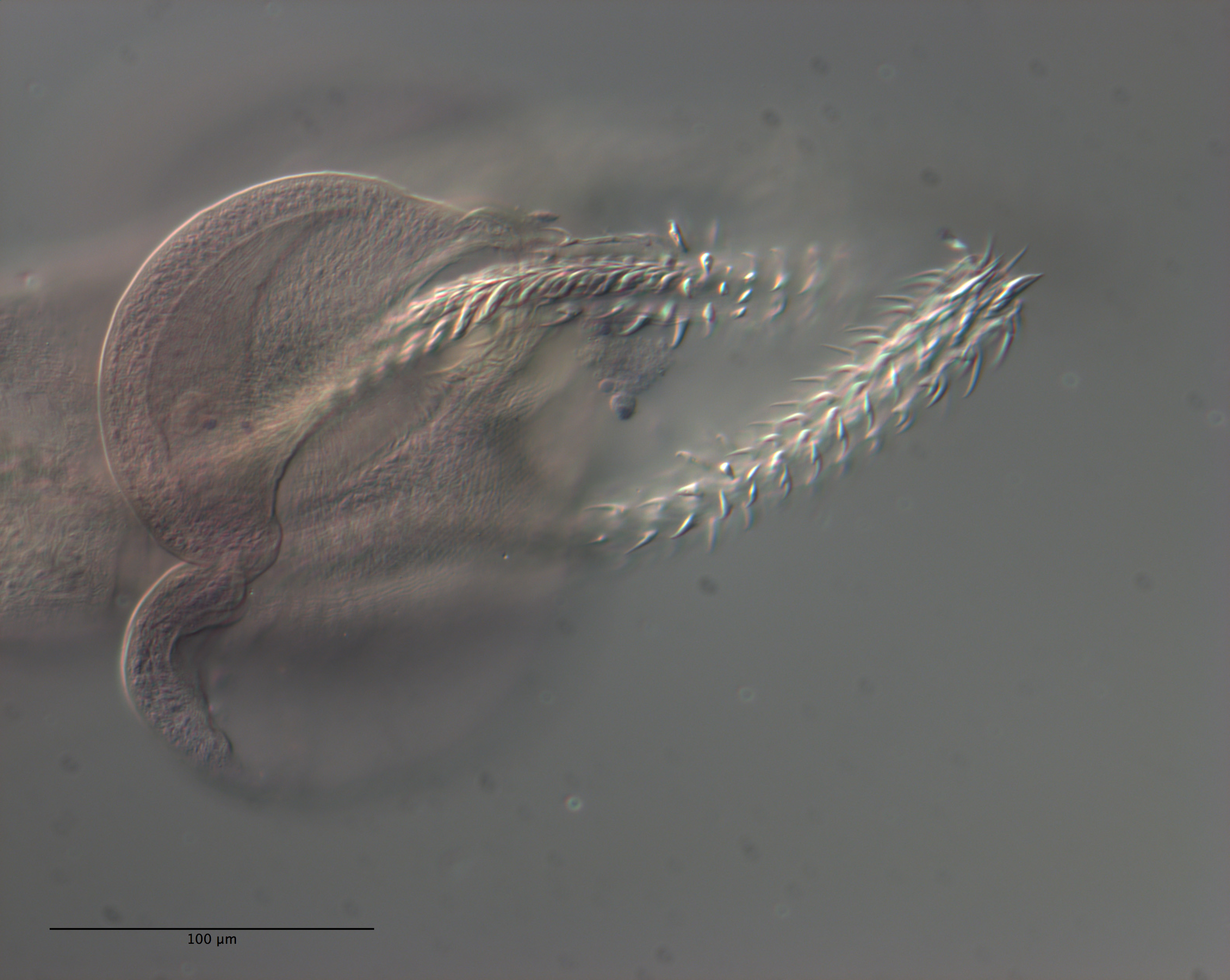
Figure 12 Line drawings of the tentacular armature of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype). (B) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface ... MoreFigure 12 Line drawings of the tentacular armature of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype). (B) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype), also showing an errant eighth hook shared between the principal rows, denoted with an asterisk (*). (C) Basal armature, bothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (D) Basal armature, antibothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (E) Comparison of metabasal hook shapes. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-12; Figure 13 Line drawings of the tentacular armature on the antibothrial surface of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. showing variation in hook number for principal rows along the tentacle. (A) Metabasal armature immediately anterior to the basal armature; nine hooks transitioning to eight hooks per
principal row (AHC 35424; voucher [paratype of Prochristianella jensenae Schaeffner & Beveridge, 2012b]). (B) Metabasal armature ~320 μm anterior to the basal armature; paired principal rows sharing an eighth hook (LRP 10603; paratype). (C) Metabasal armature ~205 μm anterior to the basal armature; eight hooks
transitioning to seven hooks per principal row (LRP 10604; paratype). (D) Metabasal armature ~305 μm anterior to the basal armature; seven hooks with an occasional eighth hook per principal row (USNM 1661589; paratype). Hooks are colored by principal row. For hooks 8(8′) and 9(9′), hooks missing their complementary hook are denoted in black font with an asterisk (*).
Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-13 |
Photo Micrograph
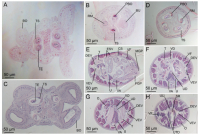
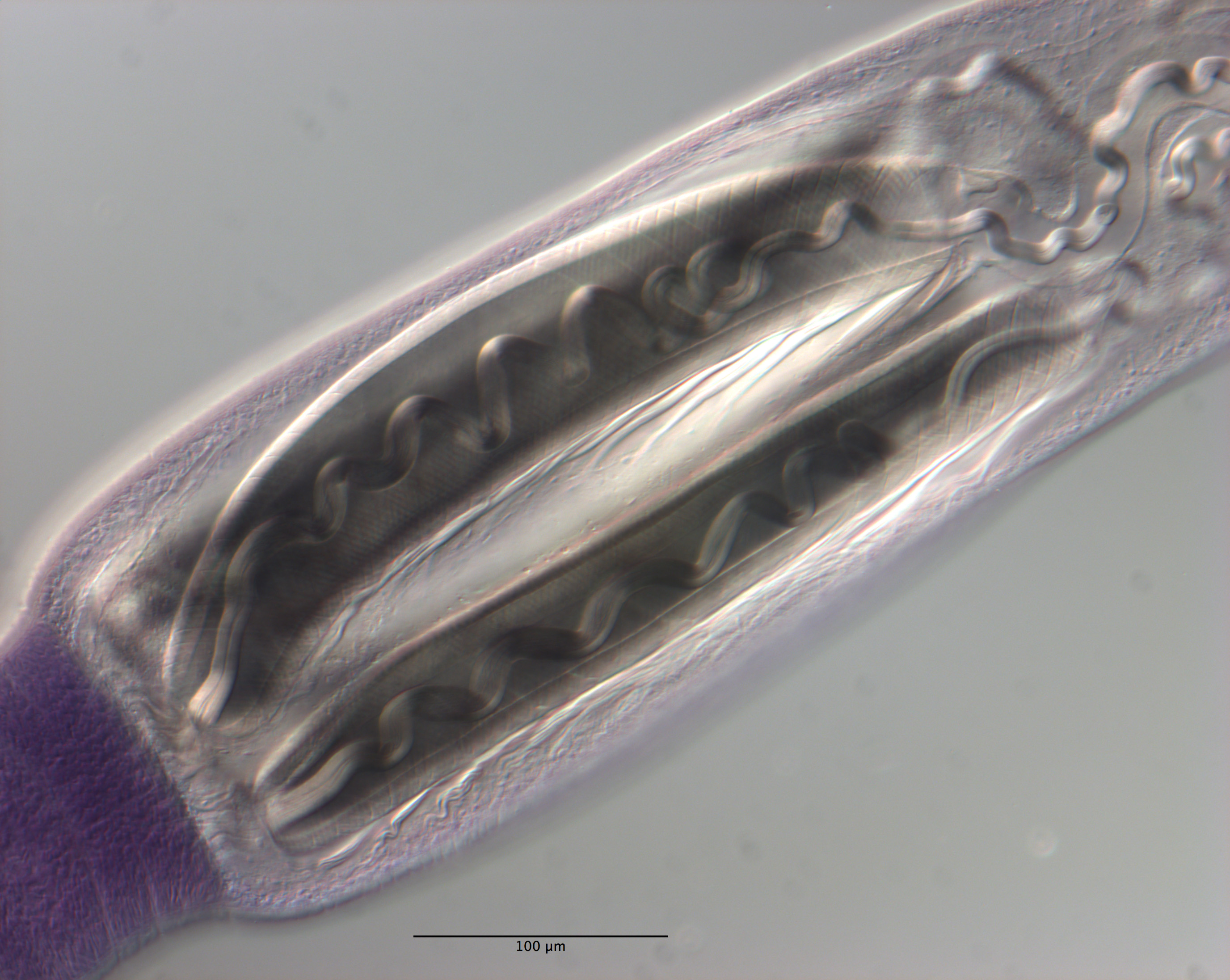
Figure 15 Light micrographs of cross-sections of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A–B) and Rhinoptericola mozambiquensis n. sp. (C–H). (A) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (B) Scolex at the level... MoreFigure 15 Light micrographs of cross-sections of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A–B) and Rhinoptericola mozambiquensis n. sp. (C–H). (A) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (B) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (C) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (D) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (E) Mature proglottid at the level of the genital pores. (F) Mature proglottid between ovary and
genital pores. (G) Mature proglottid at the anterior margin of the ovary. (H) Mature proglottid anterior to the ootype region. Abbreviations: BO, bothrium; BU, bulb; CS, cirrus sac; ESV, external seminal vesicle; DEV, dorsal excretory vessel; FGP, female genital pore; MGP, male genital pore; O, ovary; PBO, prebulbar organ; RM, retractor muscle; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; TE, tentacle; TS, tentacle sheath; U, uterus; UD, uterine duct; UTD, uterine diverticulum; VA, vagina; VEV, ventral excretory vessel; VD, vas deferens; VF, vitelline follicle. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-15 |
Scanning Electron Micrograph

Figure 14 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Scolex; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–J). (B) Bothria. (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Pr... MoreFigure 14 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Scolex; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–J). (B) Bothria. (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Proximal bothrial surface near the bothrial rim. (E) Proximal bothrial surface away from the bothrial rim. (F) Surface of the scolex proper between the bothria. (G) Surface of the scolex proper at the apex. (H) Surface of the pars vaginalis. (I) Surface of the pars bulbosa. (J) Strobilar surface. (K) Metabasal armature, external surface. (L) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface. (M) Basal armature, internal surface. (N) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with mucronate tips on the bothrial and
internal surfaces of the basal armature. (O) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with short forward protrusions on their lower surface and mucronate tips (i.e., “can opener-shaped” billhooks) on the antibothrial and external surfaces of the basal armature. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-14 |
 Global Cestode Database
Global Cestode Database





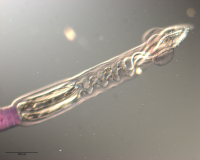
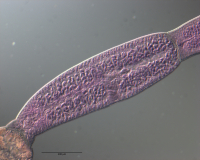
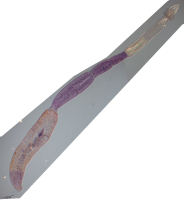
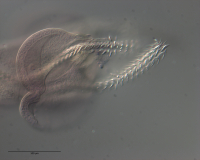
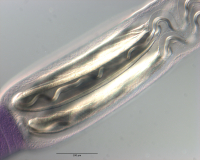

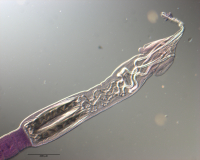
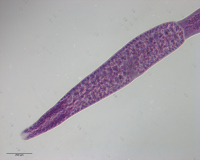

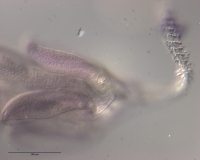
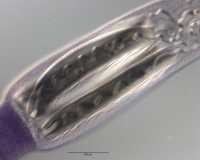

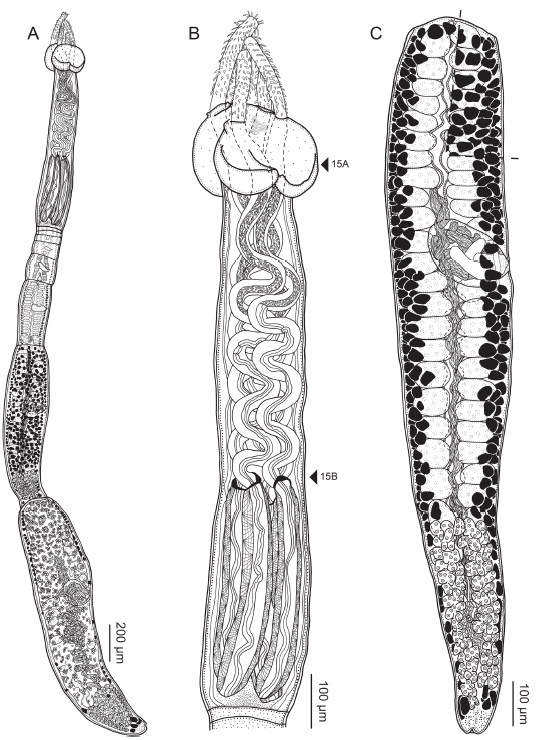 Figure 11 Line drawings of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Whole worm (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H];
holotype). (B) Scolex (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H]; holotype); arrowheads indicate the level at which the sections in Fig. 15 were taken. (C) Terminal proglottid (USNM 1661588; paratype); circumcortical vitelline follicles are drawn only on the lateral margins and in the region delimited by dashed lines. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-11
Figure 11 Line drawings of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Whole worm (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H];
holotype). (B) Scolex (MZUM[P] 2021.1 [H]; holotype); arrowheads indicate the level at which the sections in Fig. 15 were taken. (C) Terminal proglottid (USNM 1661588; paratype); circumcortical vitelline follicles are drawn only on the lateral margins and in the region delimited by dashed lines. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-11 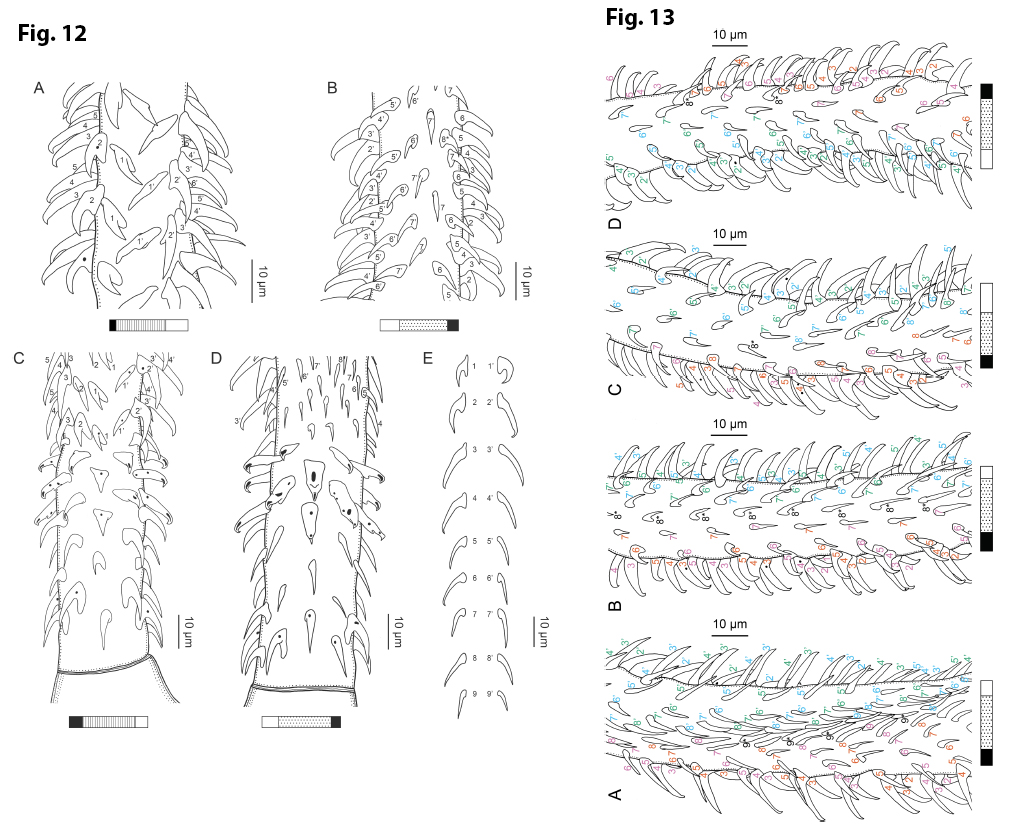 Figure 12 Line drawings of the tentacular armature of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype). (B) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype), also showing an errant eighth hook shared between the principal rows, denoted with an asterisk (*). (C) Basal armature, bothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (D) Basal armature, antibothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (E) Comparison of metabasal hook shapes. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-12; Figure 13 Line drawings of the tentacular armature on the antibothrial surface of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. showing variation in hook number for principal rows along the tentacle. (A) Metabasal armature immediately anterior to the basal armature; nine hooks transitioning to eight hooks per
principal row (AHC 35424; voucher [paratype of Prochristianella jensenae Schaeffner & Beveridge, 2012b]). (B) Metabasal armature ~320 μm anterior to the basal armature; paired principal rows sharing an eighth hook (LRP 10603; paratype). (C) Metabasal armature ~205 μm anterior to the basal armature; eight hooks
transitioning to seven hooks per principal row (LRP 10604; paratype). (D) Metabasal armature ~305 μm anterior to the basal armature; seven hooks with an occasional eighth hook per principal row (USNM 1661589; paratype). Hooks are colored by principal row. For hooks 8(8′) and 9(9′), hooks missing their complementary hook are denoted in black font with an asterisk (*).
Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-13
Figure 12 Line drawings of the tentacular armature of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype). (B) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface (USNM 1661589; paratype), also showing an errant eighth hook shared between the principal rows, denoted with an asterisk (*). (C) Basal armature, bothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (D) Basal armature, antibothrial surface (LRP 10602; paratype). (E) Comparison of metabasal hook shapes. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-12; Figure 13 Line drawings of the tentacular armature on the antibothrial surface of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. showing variation in hook number for principal rows along the tentacle. (A) Metabasal armature immediately anterior to the basal armature; nine hooks transitioning to eight hooks per
principal row (AHC 35424; voucher [paratype of Prochristianella jensenae Schaeffner & Beveridge, 2012b]). (B) Metabasal armature ~320 μm anterior to the basal armature; paired principal rows sharing an eighth hook (LRP 10603; paratype). (C) Metabasal armature ~205 μm anterior to the basal armature; eight hooks
transitioning to seven hooks per principal row (LRP 10604; paratype). (D) Metabasal armature ~305 μm anterior to the basal armature; seven hooks with an occasional eighth hook per principal row (USNM 1661589; paratype). Hooks are colored by principal row. For hooks 8(8′) and 9(9′), hooks missing their complementary hook are denoted in black font with an asterisk (*).
Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-13 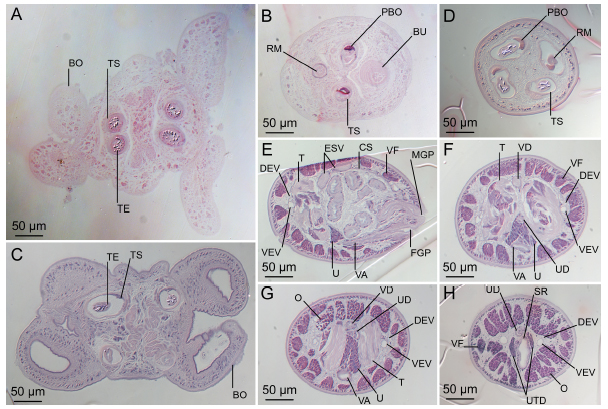 Figure 15 Light micrographs of cross-sections of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A–B) and Rhinoptericola mozambiquensis n. sp. (C–H). (A) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (B) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (C) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (D) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (E) Mature proglottid at the level of the genital pores. (F) Mature proglottid between ovary and
genital pores. (G) Mature proglottid at the anterior margin of the ovary. (H) Mature proglottid anterior to the ootype region. Abbreviations: BO, bothrium; BU, bulb; CS, cirrus sac; ESV, external seminal vesicle; DEV, dorsal excretory vessel; FGP, female genital pore; MGP, male genital pore; O, ovary; PBO, prebulbar organ; RM, retractor muscle; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; TE, tentacle; TS, tentacle sheath; U, uterus; UD, uterine duct; UTD, uterine diverticulum; VA, vagina; VEV, ventral excretory vessel; VD, vas deferens; VF, vitelline follicle. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-15
Figure 15 Light micrographs of cross-sections of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A–B) and Rhinoptericola mozambiquensis n. sp. (C–H). (A) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (B) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (C) Scolex at the level of the bothria. (D) Scolex at the level of the prebulbar organs. (E) Mature proglottid at the level of the genital pores. (F) Mature proglottid between ovary and
genital pores. (G) Mature proglottid at the anterior margin of the ovary. (H) Mature proglottid anterior to the ootype region. Abbreviations: BO, bothrium; BU, bulb; CS, cirrus sac; ESV, external seminal vesicle; DEV, dorsal excretory vessel; FGP, female genital pore; MGP, male genital pore; O, ovary; PBO, prebulbar organ; RM, retractor muscle; SR, seminal receptacle; T, testis; TE, tentacle; TS, tentacle sheath; U, uterus; UD, uterine duct; UTD, uterine diverticulum; VA, vagina; VEV, ventral excretory vessel; VD, vas deferens; VF, vitelline follicle. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-15 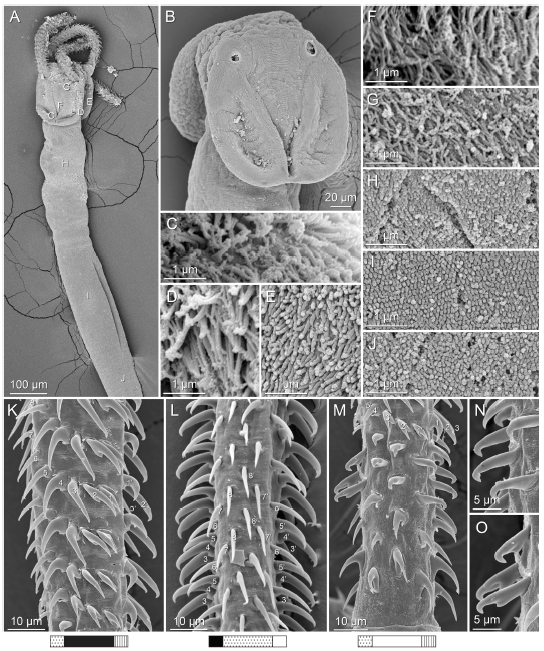 Figure 14 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Scolex; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–J). (B) Bothria. (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Proximal bothrial surface near the bothrial rim. (E) Proximal bothrial surface away from the bothrial rim. (F) Surface of the scolex proper between the bothria. (G) Surface of the scolex proper at the apex. (H) Surface of the pars vaginalis. (I) Surface of the pars bulbosa. (J) Strobilar surface. (K) Metabasal armature, external surface. (L) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface. (M) Basal armature, internal surface. (N) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with mucronate tips on the bothrial and
internal surfaces of the basal armature. (O) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with short forward protrusions on their lower surface and mucronate tips (i.e., “can opener-shaped” billhooks) on the antibothrial and external surfaces of the basal armature. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-14
Figure 14 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola schaeffneri n. sp. (A) Scolex; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–J). (B) Bothria. (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Proximal bothrial surface near the bothrial rim. (E) Proximal bothrial surface away from the bothrial rim. (F) Surface of the scolex proper between the bothria. (G) Surface of the scolex proper at the apex. (H) Surface of the pars vaginalis. (I) Surface of the pars bulbosa. (J) Strobilar surface. (K) Metabasal armature, external surface. (L) Metabasal armature, antibothrial surface. (M) Basal armature, internal surface. (N) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with mucronate tips on the bothrial and
internal surfaces of the basal armature. (O) Falcate, erect, dorsoventrally flattened billhooks with short forward protrusions on their lower surface and mucronate tips (i.e., “can opener-shaped” billhooks) on the antibothrial and external surfaces of the basal armature. Full-size image DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-14