Cestode Scientific Name
| Species ID | 14431 |
|---|---|
| Order | Trypanorhyncha |
| Family | Rhinoptericolidae |
| Subfamily | |
| Genus | Rhinoptericola |
| Species | butlerae |
| Authority | (Beveridge & Campbell, 1988) Herzog & Jensen, 2022 |
| Taxonomic Status | Valid |
| Valid Name | |
| Synonyms | Shirleyrhynchus butlerae Beveridge & Campbell, 1988 |
| Genus Record | No |
| Type Species | Yes |
| Verified | Yes |
| Verified By | K. S. Herzog |
| Citation(s) |
Beveridge, I. and R. A. Campbell. 1988. Cetorhinicola n.g., Shirleyrhynchus n.g. and Stragulorhynchus n.g., three new genera of trypanorhynch cestodes from elasmobranchs in Australian waters. Systematic Parasitology 12: 47-60. (4251) Download PDFHerzog, K. S. and K. Jensen. 2022. A synergistic, global approach to revising the trypanorhynch tapeworm family Rhinoptericolidae (Trypanobatoida). PeerJ Life & Environment 10:e12865: 83 pp. (7426) Download PDF |
| Redescription | |
| Scientific Name Notes | This species was first allocated tentatively to the Gilquiniidae by Beveridge & Campbell (1988) and then to the Shirleyrhynchidae by Campbell & Beveridge (1994). When Beveridge & Campbell (1998) moved Tetrarhynchus aetobatidis Shipley & Hornell, 1906 to the genus Shirleyrhynchus as Shirleyrhynchus aetobatidis (Shipley & Hornell, 1906) Beveridge & Campbell, 1998, they synonymized S. aetobatidis and Shirleyrhynchus butlerae Beveridge & Campbell, 1988, briefly making S. butlerae and junior synonym of S. aetobatidis. However, Schaeffner (2016) resurrected S. butlerae from synonomy. |
Record Data
| Date (MM/DD/YYYY) | Action | User Name |
|---|---|---|
| 02/17/2022 | Created | B. Barbeau |
| 02/17/2022 | Modified | B. Barbeau |
| 02/18/2022 | Modified | B. Barbeau |
| 02/21/2022 | Modified | K. Herzog |
Type Host
| Host Class | Elasmobranchii | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host Order | Myliobatiformes | ||||||
| Host Family | Dasyatidae | ||||||
|
Type Host (Literal) |
|
||||||
|
Type Host (Valid) |
|
||||||
| Additional Host(s) | Dasyatis sephen; Additional hosts from redescription: Hemitrygon bennetti (Müller & Henle, 1841), Himantura tutul Borsa, Durand, Shen, Alyza, Solihin & Berrebi, 2013, Maculabatis gerrardi (Gray, 1851), Pastinachus ater (Macleay, 1883), and Pastinachus solocirostris Last, Manjaji & Yearsley, 2005 (Dasyatidae: Myliobatiformes); Rhinoptera javanica Müller & Henle, 1841 and Rhinoptera neglecta Ogilby, 1912 (Rhinopteridae: Myliobatiformes); Chiloscyllium punctatum Müller & Henle, 1838 (Hemiscyliidae; Orectolobiformes) | ||||||
| Site in Host | spiral intestine | ||||||
| Host Notes |
Type Locality
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| Body of Water | Moreton Bay, Coral Sea, Deception Bay |
| Island(s) | |
| City/Region | Queensland |
| Coordinates | |
| DD Latitude | |
| DD Longitude | |
| Additional Localities | Fog Bay, NT, Australia; Additional localities from redescription: Arafura Sea, Australia: East of Wessel Islands (11°17′44″S, 136°59′48″E), Northern Territory. Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia: Weipa (12°35′11″S, 141°42′34″E), Queensland. Timor Sea, Australia: Dundee Beach (12°45′33″S, 130°21′7″E), Northern Territory, Fog Bay. Java Sea, Indonesia: Gusungnge near Pagatan market (03°36′46.10″S, 115°55′05.10″E), South Kalimantan; and Pagatan market (03°36′36.00″S, 115°54′59.40″E), South Kalimantan. Makassar Strait, Indonesia: Muara Pasir (01°45′58.92″S, 116°23′36.09″E), East Kalimantan. South China Sea, Malaysia: Mukah (02°53′52.16″N, 112°05′44.12″E), Sarawak. South China Sea, Viet Nam: Cat Ba (20°43′31.1″N, 107°02′54.9″E), Haiphong Province, Gulf of Tonkin; and Long Hai (10°22′60.00″N, 107°13′60.00″E), Ba Ria Province. |
| Locality Notes | Type locality given as: "Type localities: Moreton and Deception Bays, Queensland" (Beveridge and Campbell, 1988) |
Specimens
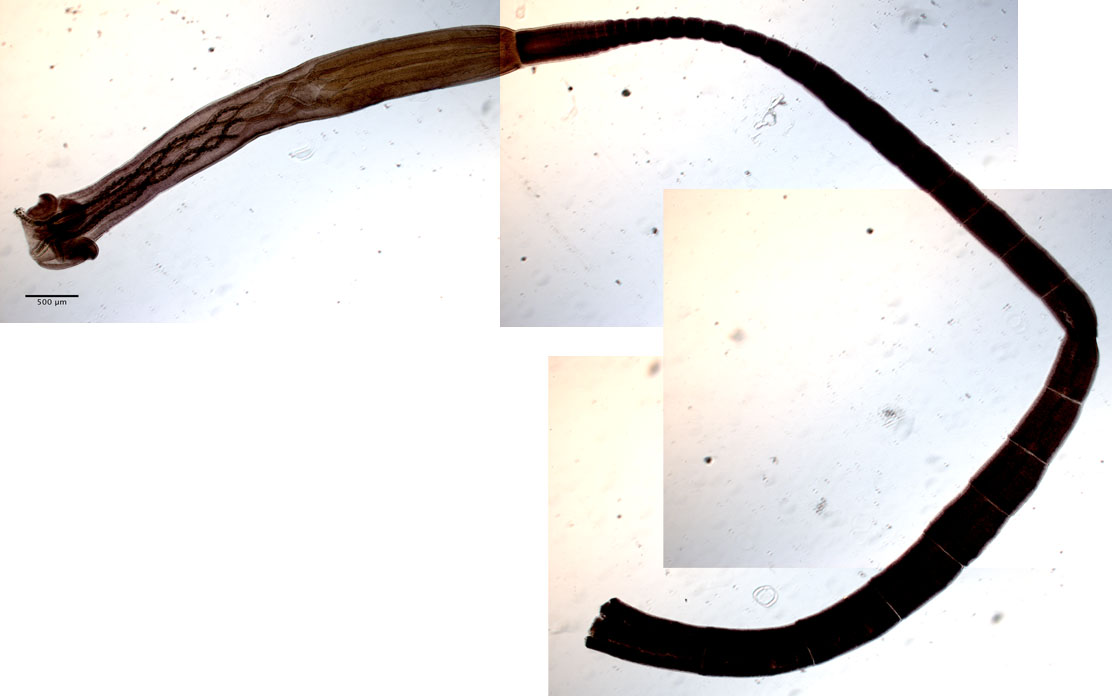
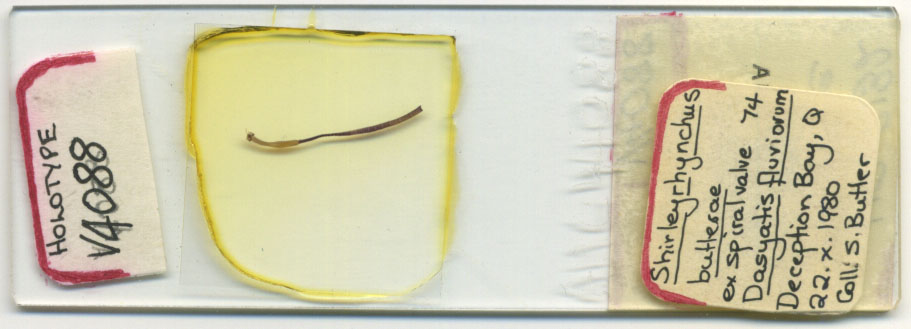
| Type Material | AHC 44088 [SAM V4088] (holotype); AHC 22773 [SAM S2773], BMNH 1987.5.1.1, USNM 1375081 [USNPC 79701] (paratypes) |
|---|---|
| Total Number of Type Specimens | 1 holotype, 9 paratypes |
| Voucher Material | LRP 10559–10569 (Schaeffner & Beveridge, 2014), LRP 10547–10549, LRP 10551, and LRP 10554–10557 (this study), LRP 10550, LRP 10552, LRP 10553, and LRP 10558 (hologenophores, this study); QM G239454–G239456 (this study). |
| Specimen Notes | Redescription based on holotype, six paratypes, and 10 voucher specimens: one gravid worm, one mature worm, three immature worms, and four complete scoleces and one partial scolex prepared for SEM; type specimen accession numbers in brackets are original numbers. |
Data are given as in original description unless otherwise indicated.
 Global Cestode Database
Global Cestode Database

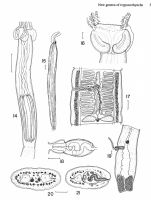
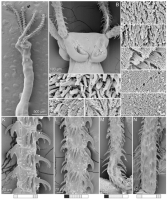





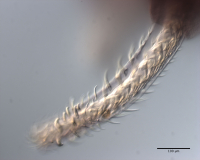
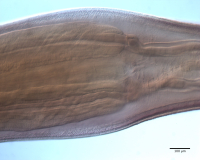

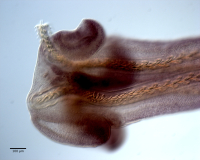


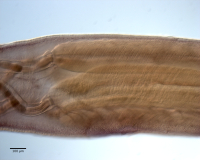

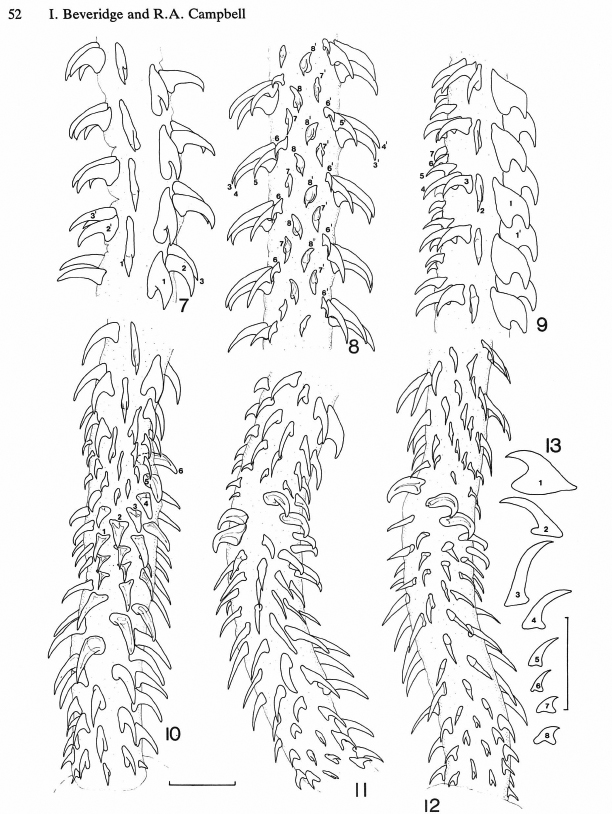
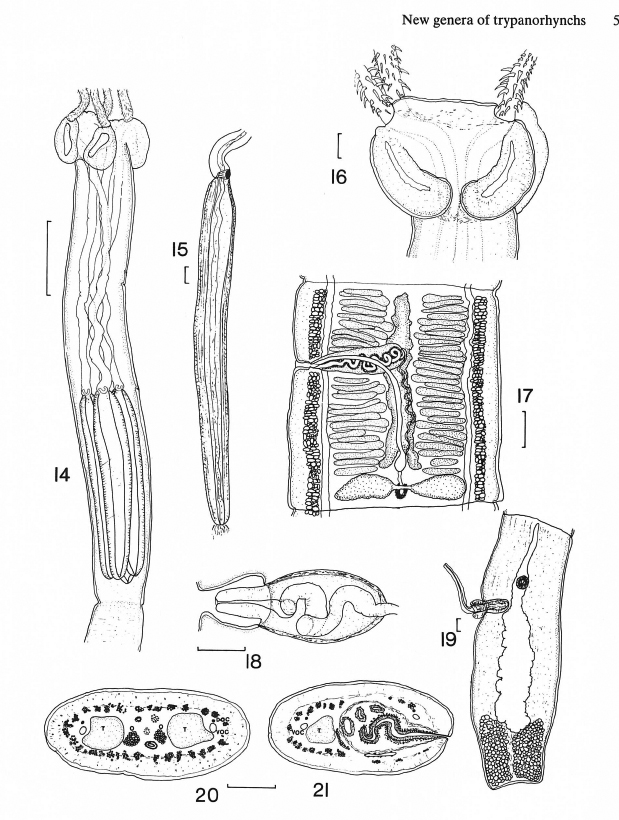
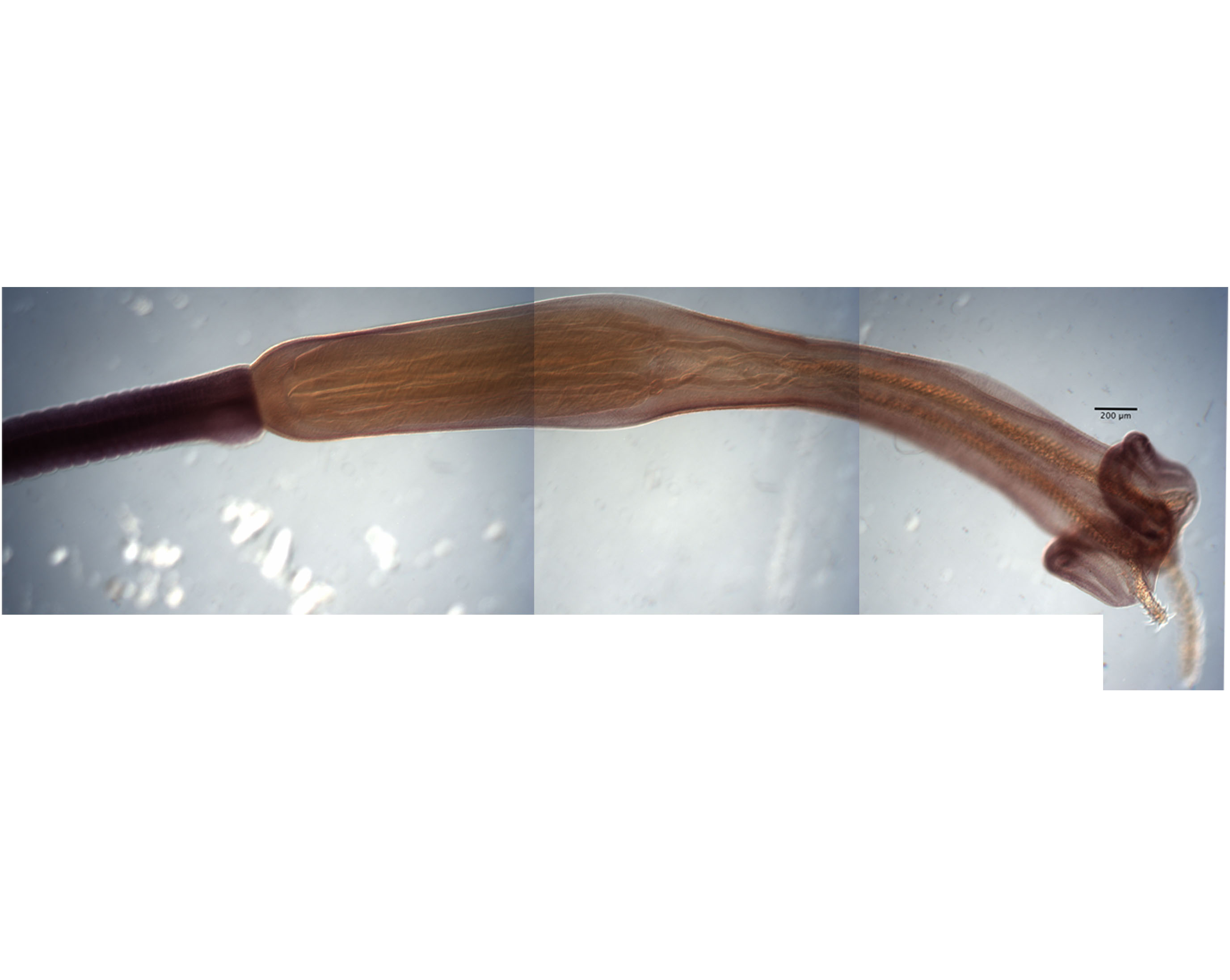
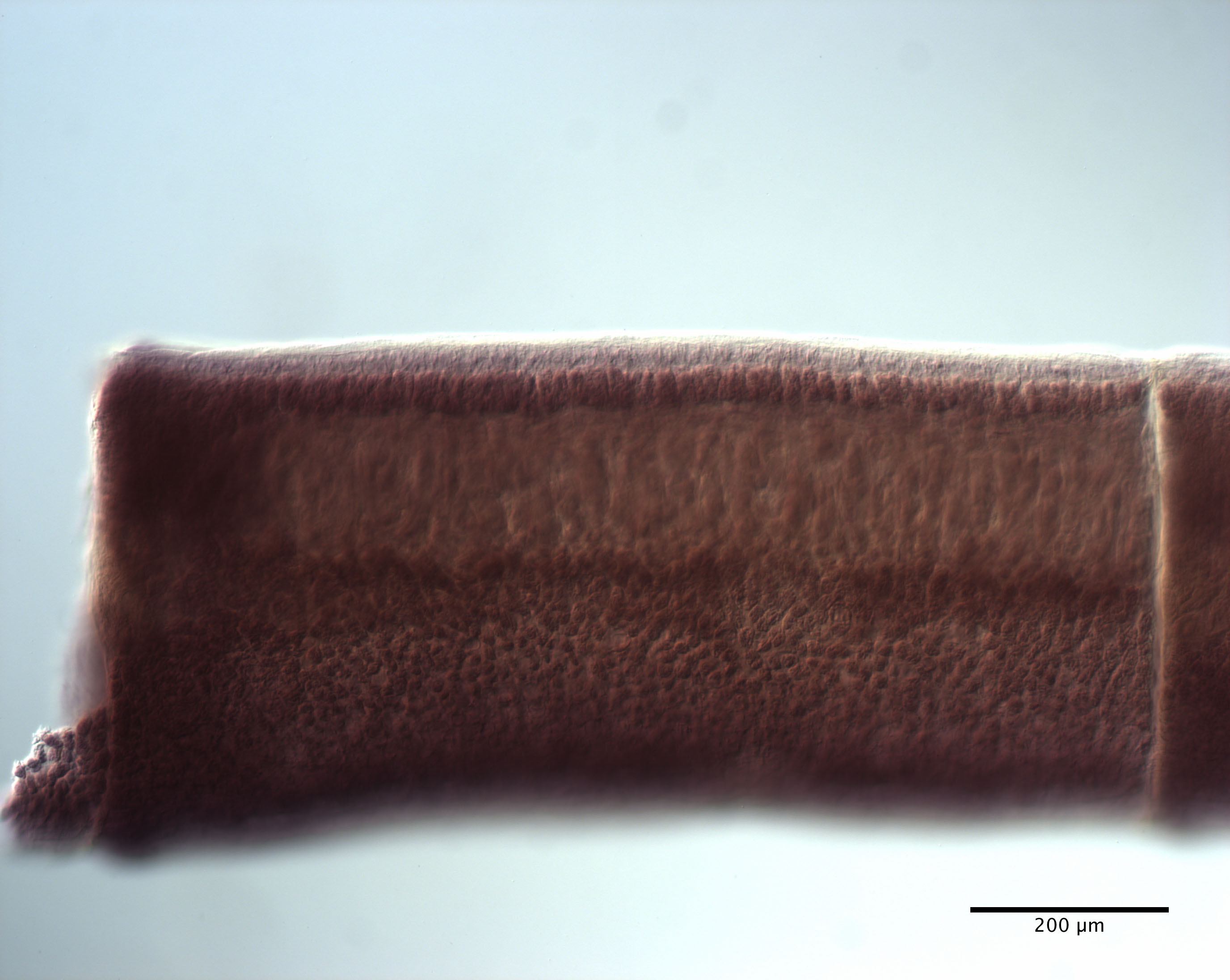
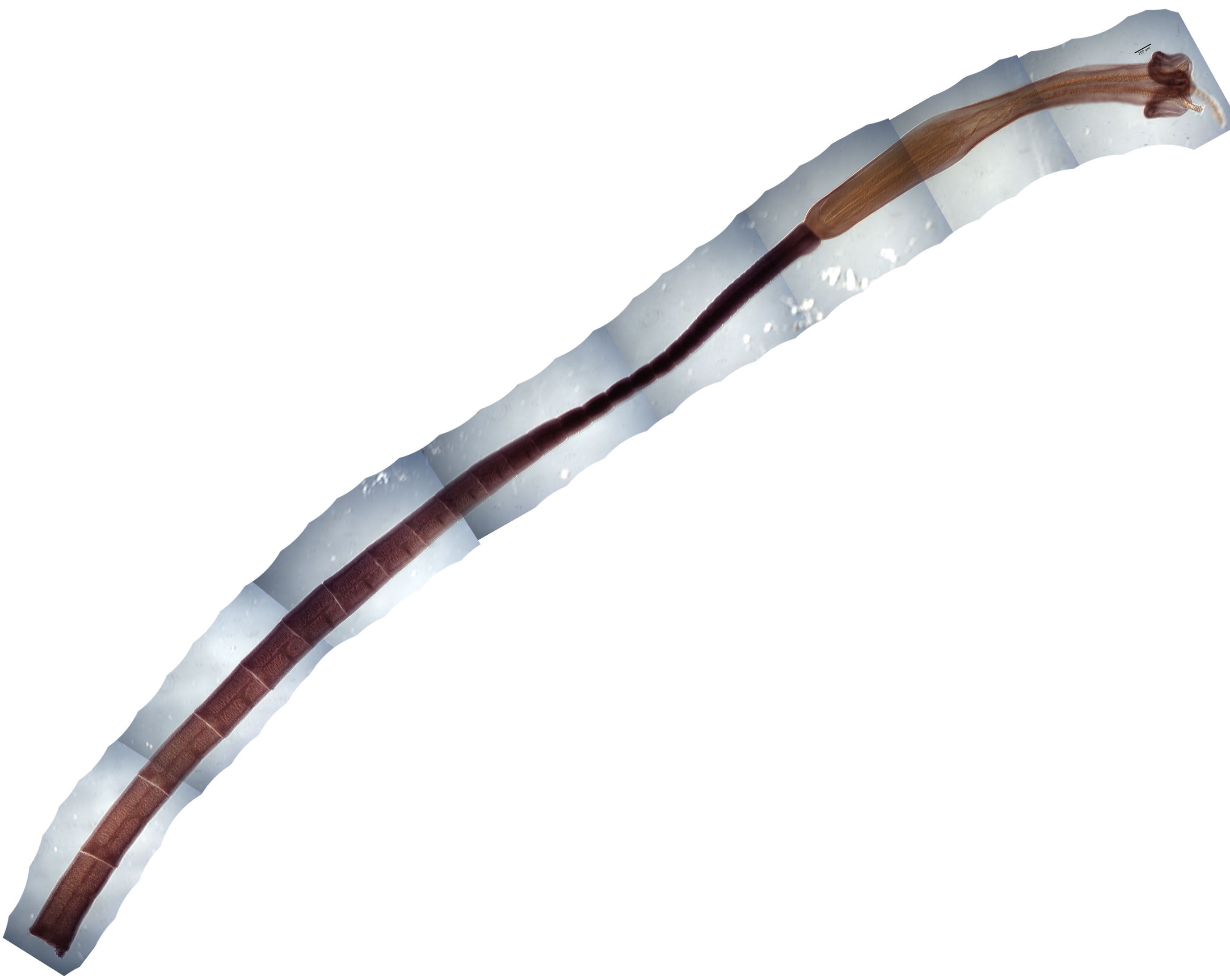
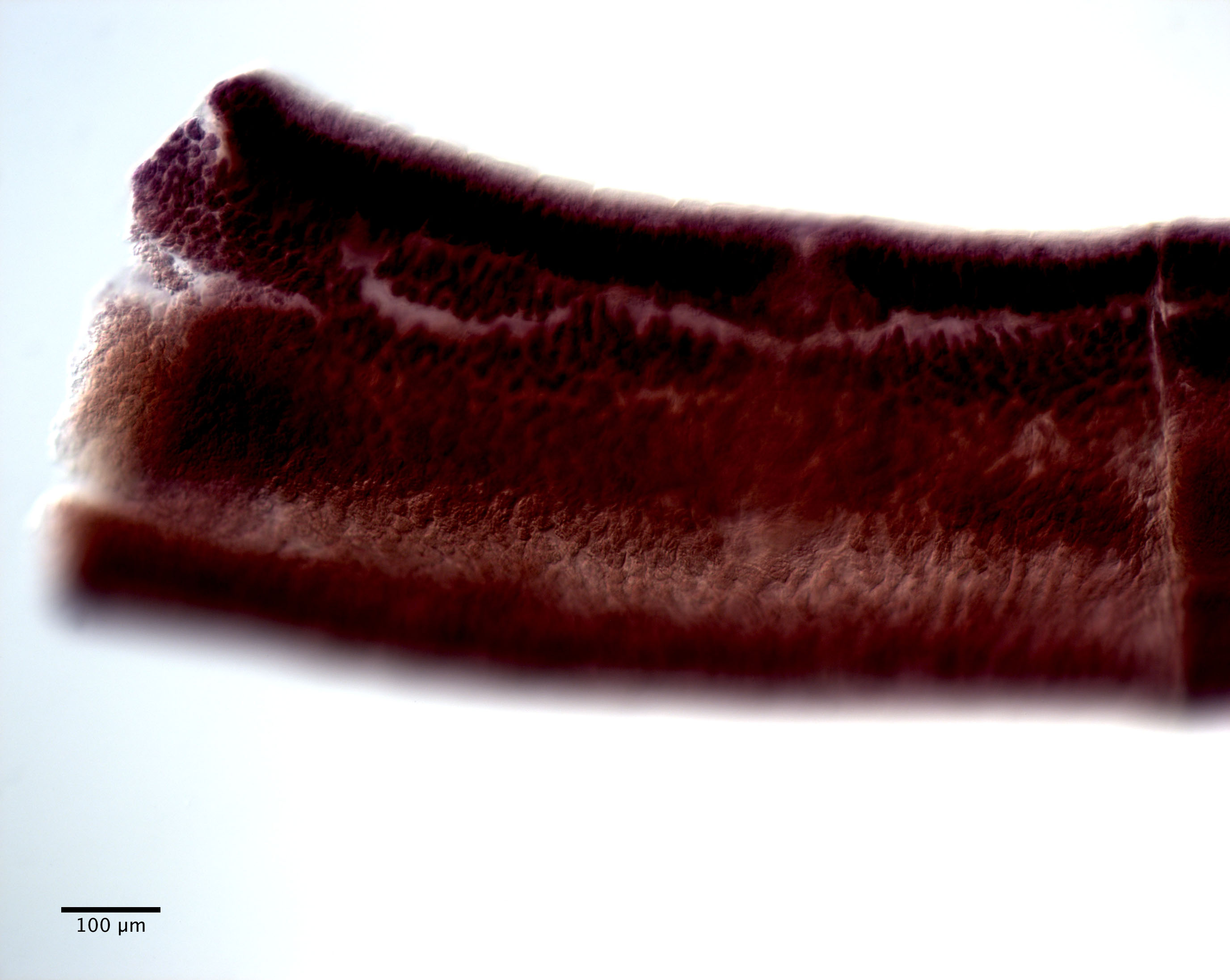
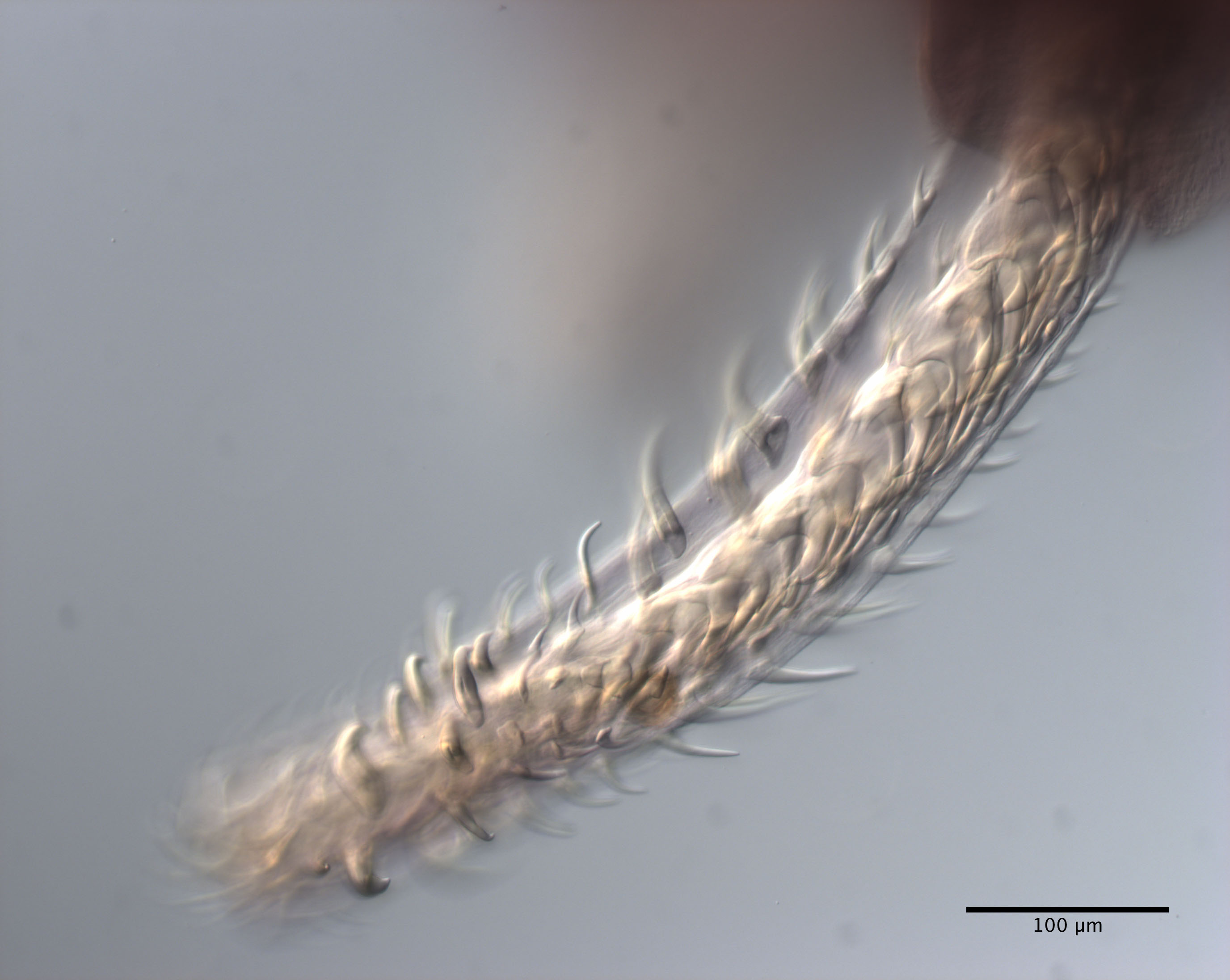
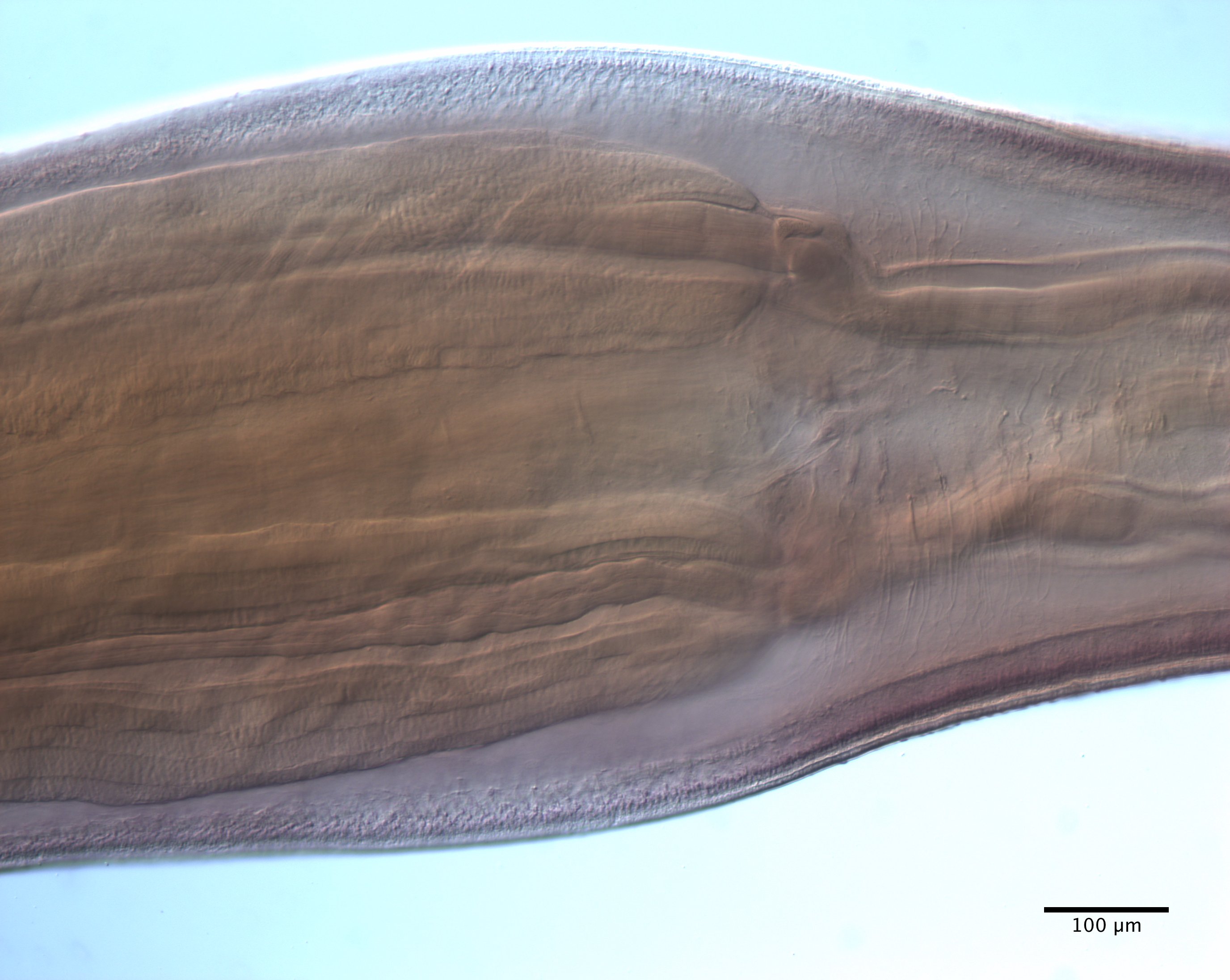
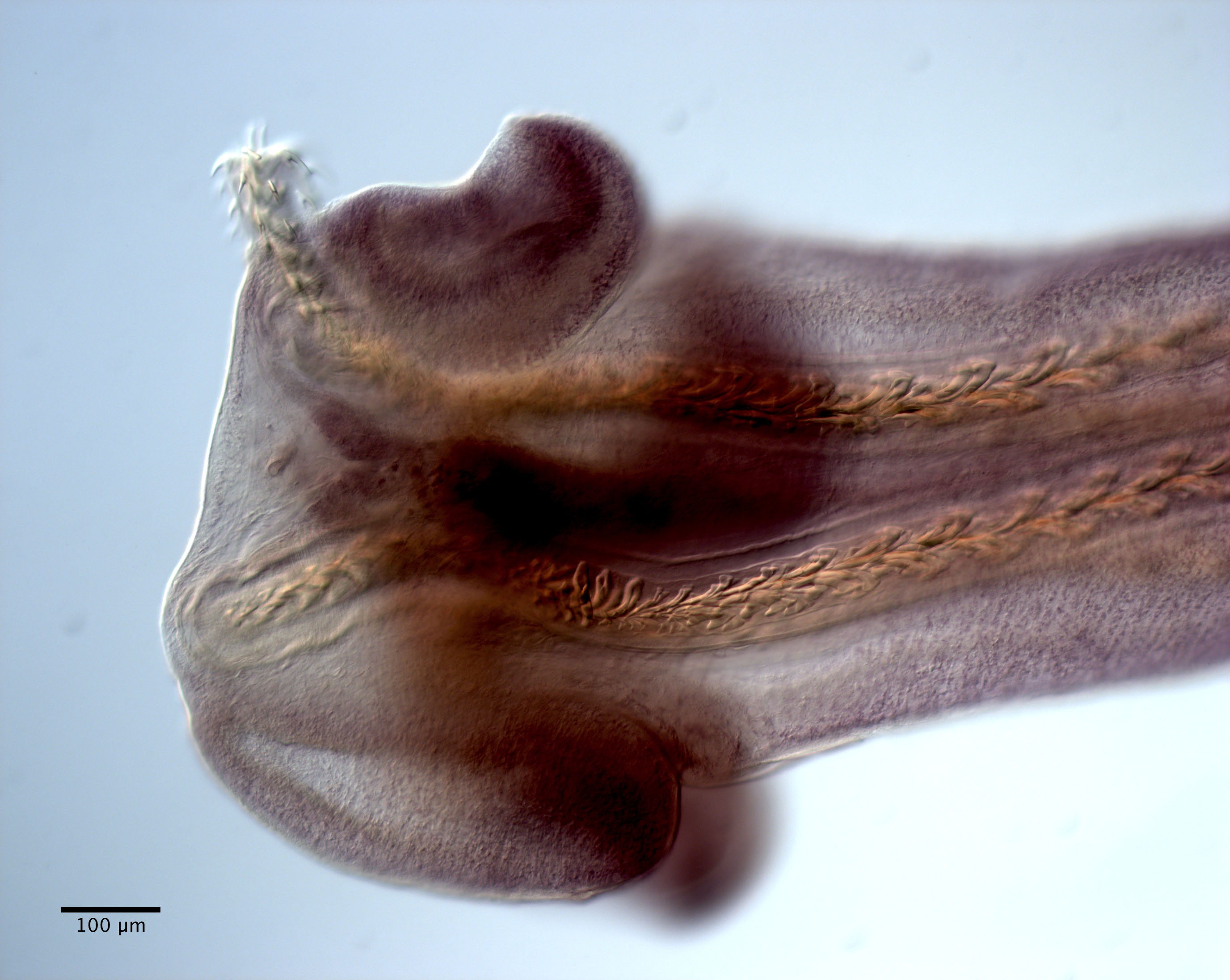
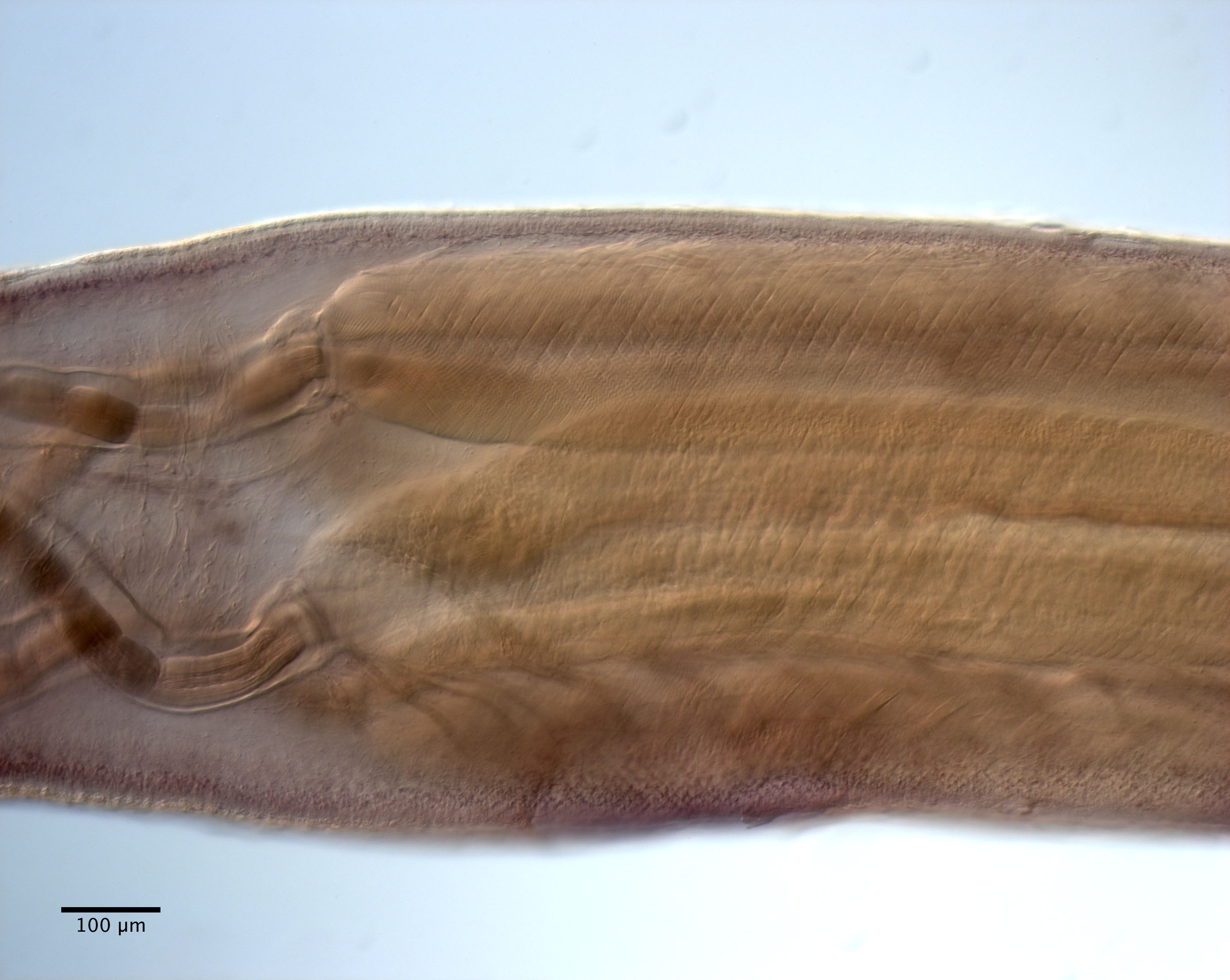
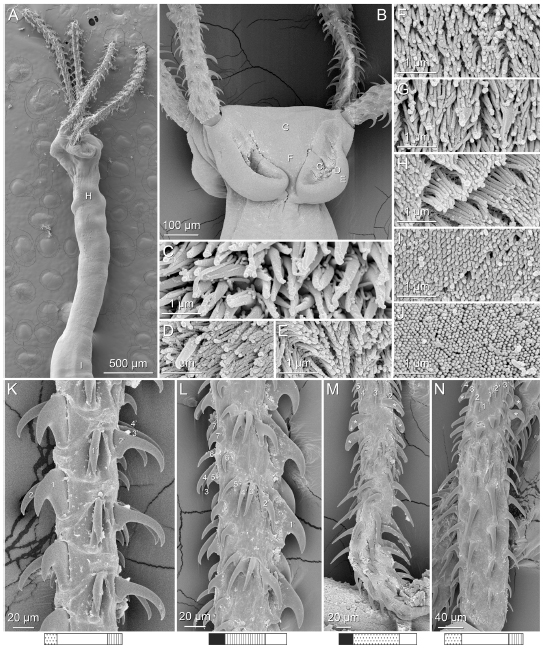 From Herzog & Jensen, 2022 (Cit# 7426). Figure 7 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola butlerae (Beveridge & Campbell, 1988) n. comb. (A) Scolex; small letter indicates the location of details shown in (H–I). (B) Bothria and basal armature; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–G). (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Proximal bothrial surface near the bothrial rim. (E) Proximal bothria surface away from the bothrial
rim. (F) Surface of the scolex proper between the bothria. (G) Surface of the scolex proper at the apex. (H) Surface of the pars vaginalis. (I) Surface of the pars bulbosa. (J) Strobilar surface. (K) Metabasal armature, internal surface. (L) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface. (M) Basal armature, antibothrial
surface. (N) Basal armature, internal surface. Asterisks (*) in M and N indicate macrohooks.
Full-size images DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-7
From Herzog & Jensen, 2022 (Cit# 7426). Figure 7 Scanning electron micrographs of Rhinoptericola butlerae (Beveridge & Campbell, 1988) n. comb. (A) Scolex; small letter indicates the location of details shown in (H–I). (B) Bothria and basal armature; small letters indicate the location of details shown in (C–G). (C) Distal bothrial surface. (D) Proximal bothrial surface near the bothrial rim. (E) Proximal bothria surface away from the bothrial
rim. (F) Surface of the scolex proper between the bothria. (G) Surface of the scolex proper at the apex. (H) Surface of the pars vaginalis. (I) Surface of the pars bulbosa. (J) Strobilar surface. (K) Metabasal armature, internal surface. (L) Metabasal armature, bothrial surface. (M) Basal armature, antibothrial
surface. (N) Basal armature, internal surface. Asterisks (*) in M and N indicate macrohooks.
Full-size images DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12865/fig-7