Line Drawing 1
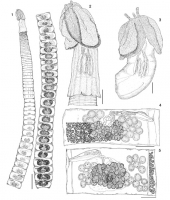
Figs 1–5. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp.: 1, entire worm, circum-medullar vitelline follicles not drawn to allow the view of internal organs (scale bar = 1 mm); 2, scolex of adult worm (scale bar = 20... MoreFigs 1–5. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp.: 1, entire worm, circum-medullar vitelline follicles not drawn to allow the view of internal organs (scale bar = 1 mm); 2, scolex of adult worm (scale bar = 200µm); 3, plerocercoid (scale bar ¼ 200µm); 4, mature proglottid, dorsal view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm); 5, gravid proglottid, ventral view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm). |
Line Drawing 2
Figs 6–8. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., cross-sections of a gravid proglottid (scale bar = 150µm): 6, at the level of the genital pore; 7,
at level of the ovary, anterior to ovarian isthmus; 8, at ... MoreFigs 6–8. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., cross-sections of a gravid proglottid (scale bar = 150µm): 6, at the level of the genital pore; 7,
at level of the ovary, anterior to ovarian isthmus; 8, at level of Mehlis’ gland, posterior to ovarian isthmus. cs, Cirrus sac; ga, genital atrium; dod, osmoregulatory duct; mg, Mehlis’ gland; ov, ovary; t, testis; u, uterus; va, vagina; vd, vas deferens; vf, vitelline follicles; vod, ventral osmoregulatory duct. Figs 22–27. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., tentacular armature. 22, Antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm); 23, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 24, external surface of tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 25, internal surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm). 26–27, Profiles of hooks of basal and metabasal
armature of Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp. (scale bar = 20µm): 26, bothrial surface, uncinate hooks with rounded bases; 27, antibothrial surface, uncinate hooks with elongate bases. r1, row 1; r2, row 2; r5, row 5; r10, row 10; r15, row 15. |
Photo Micrograph
|
Scanning Electron Micrograph

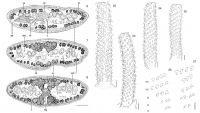
Figs 9–21. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs. 9, Dorso-ventral view of the scolex, adult (scale bar = 300µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 10, ... MoreFigs 9–21. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs. 9, Dorso-ventral view of the scolex, adult (scale bar = 300µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 10, 12, 13 and 20; 10, lateral and posterior bothrial margins, adult (scale bar = 30 µm); 11, distal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm); 12, posterior margin of bothria, adult (scale bar = 25µm); 13, detail of lateral bothrial margin, adult (scale bar = 5µm); 14, hamulate spinitriches on the posterior bothrial margin, adult
(scale bar = 10 µm); 15, proximal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 3 µm); 16, lateral view of the scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 150µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 11, 15, 18 and 21; 17, apex of scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 1 µm); 18, hamulate spinitriches in the posterior margin of bothria, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15µm); 19, pars vaginalis, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2µm); 20, surface of pars bulbosa, adult (scale bar = 1.5µm); 21, distal bothrial surface near posterior margin of bothria,
plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm). Figs 28–34. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs: 28, antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20 µm); 29, detail of the metabasal armature, antibothrial surface showing an interrupted row of hooks at the level of row 8 (arrow), plerocercoid (scale bar = 7µm); 30, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm); 31, metabasal hooks, bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15 µm); 32, metabasal region, antibothrial surface, adult (scale bar = 7µm); 33, basal hooks, antibothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 5µm); 34, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm). |
 Global Cestode Database
Global Cestode Database




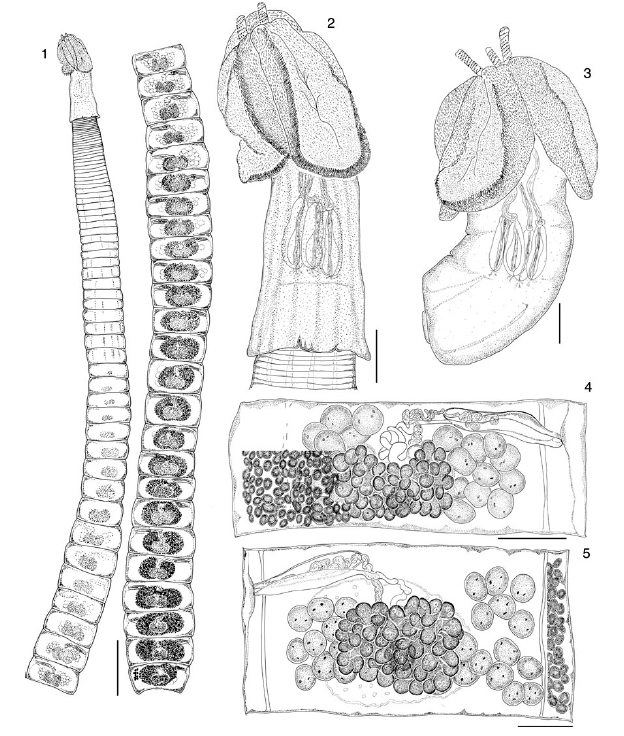 Figs 1–5. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp.: 1, entire worm, circum-medullar vitelline follicles not drawn to allow the view of internal organs (scale bar = 1 mm); 2, scolex of adult worm (scale bar = 200µm); 3, plerocercoid (scale bar ¼ 200µm); 4, mature proglottid, dorsal view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm); 5, gravid proglottid, ventral view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm).
Figs 1–5. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp.: 1, entire worm, circum-medullar vitelline follicles not drawn to allow the view of internal organs (scale bar = 1 mm); 2, scolex of adult worm (scale bar = 200µm); 3, plerocercoid (scale bar ¼ 200µm); 4, mature proglottid, dorsal view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm); 5, gravid proglottid, ventral view, circum-medullar vitelline follicles partially drawn (scale bar = 150µm). 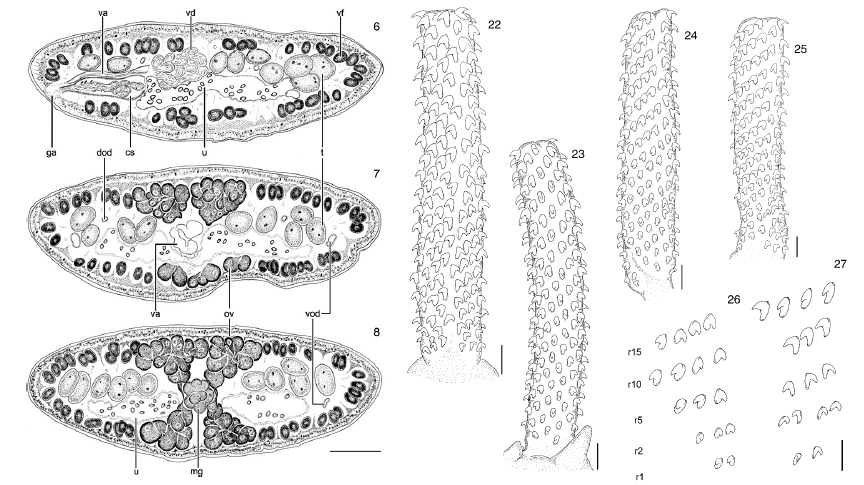 Figs 6–8. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., cross-sections of a gravid proglottid (scale bar = 150µm): 6, at the level of the genital pore; 7,
at level of the ovary, anterior to ovarian isthmus; 8, at level of Mehlis’ gland, posterior to ovarian isthmus. cs, Cirrus sac; ga, genital atrium; dod, osmoregulatory duct; mg, Mehlis’ gland; ov, ovary; t, testis; u, uterus; va, vagina; vd, vas deferens; vf, vitelline follicles; vod, ventral osmoregulatory duct. Figs 22–27. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., tentacular armature. 22, Antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm); 23, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 24, external surface of tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 25, internal surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm). 26–27, Profiles of hooks of basal and metabasal
armature of Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp. (scale bar = 20µm): 26, bothrial surface, uncinate hooks with rounded bases; 27, antibothrial surface, uncinate hooks with elongate bases. r1, row 1; r2, row 2; r5, row 5; r10, row 10; r15, row 15.
Figs 6–8. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., cross-sections of a gravid proglottid (scale bar = 150µm): 6, at the level of the genital pore; 7,
at level of the ovary, anterior to ovarian isthmus; 8, at level of Mehlis’ gland, posterior to ovarian isthmus. cs, Cirrus sac; ga, genital atrium; dod, osmoregulatory duct; mg, Mehlis’ gland; ov, ovary; t, testis; u, uterus; va, vagina; vd, vas deferens; vf, vitelline follicles; vod, ventral osmoregulatory duct. Figs 22–27. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., tentacular armature. 22, Antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm); 23, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 24, external surface of tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25µm); 25, internal surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 25 µm). 26–27, Profiles of hooks of basal and metabasal
armature of Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp. (scale bar = 20µm): 26, bothrial surface, uncinate hooks with rounded bases; 27, antibothrial surface, uncinate hooks with elongate bases. r1, row 1; r2, row 2; r5, row 5; r10, row 10; r15, row 15. 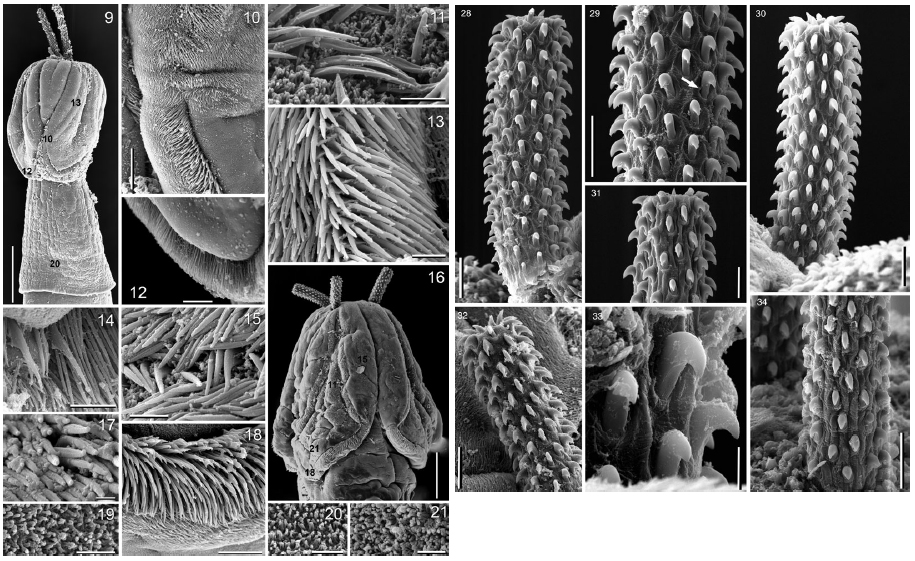 Figs 9–21. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs. 9, Dorso-ventral view of the scolex, adult (scale bar = 300µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 10, 12, 13 and 20; 10, lateral and posterior bothrial margins, adult (scale bar = 30 µm); 11, distal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm); 12, posterior margin of bothria, adult (scale bar = 25µm); 13, detail of lateral bothrial margin, adult (scale bar = 5µm); 14, hamulate spinitriches on the posterior bothrial margin, adult
(scale bar = 10 µm); 15, proximal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 3 µm); 16, lateral view of the scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 150µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 11, 15, 18 and 21; 17, apex of scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 1 µm); 18, hamulate spinitriches in the posterior margin of bothria, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15µm); 19, pars vaginalis, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2µm); 20, surface of pars bulbosa, adult (scale bar = 1.5µm); 21, distal bothrial surface near posterior margin of bothria,
plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm). Figs 28–34. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs: 28, antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20 µm); 29, detail of the metabasal armature, antibothrial surface showing an interrupted row of hooks at the level of row 8 (arrow), plerocercoid (scale bar = 7µm); 30, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm); 31, metabasal hooks, bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15 µm); 32, metabasal region, antibothrial surface, adult (scale bar = 7µm); 33, basal hooks, antibothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 5µm); 34, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm).
Figs 9–21. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs. 9, Dorso-ventral view of the scolex, adult (scale bar = 300µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 10, 12, 13 and 20; 10, lateral and posterior bothrial margins, adult (scale bar = 30 µm); 11, distal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm); 12, posterior margin of bothria, adult (scale bar = 25µm); 13, detail of lateral bothrial margin, adult (scale bar = 5µm); 14, hamulate spinitriches on the posterior bothrial margin, adult
(scale bar = 10 µm); 15, proximal bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 3 µm); 16, lateral view of the scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 150µm), small numbers indicate locations of details shown in figs 11, 15, 18 and 21; 17, apex of scolex, plerocercoid (scale bar = 1 µm); 18, hamulate spinitriches in the posterior margin of bothria, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15µm); 19, pars vaginalis, plerocercoid (scale bar = 2µm); 20, surface of pars bulbosa, adult (scale bar = 1.5µm); 21, distal bothrial surface near posterior margin of bothria,
plerocercoid (scale bar = 2 µm). Figs 28–34. Heteronybelinia mattisi n. sp., scanning electron micrographs: 28, antibothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20 µm); 29, detail of the metabasal armature, antibothrial surface showing an interrupted row of hooks at the level of row 8 (arrow), plerocercoid (scale bar = 7µm); 30, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm); 31, metabasal hooks, bothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 15 µm); 32, metabasal region, antibothrial surface, adult (scale bar = 7µm); 33, basal hooks, antibothrial surface, plerocercoid (scale bar = 5µm); 34, bothrial surface of the tentacle, plerocercoid (scale bar = 20µm). 

